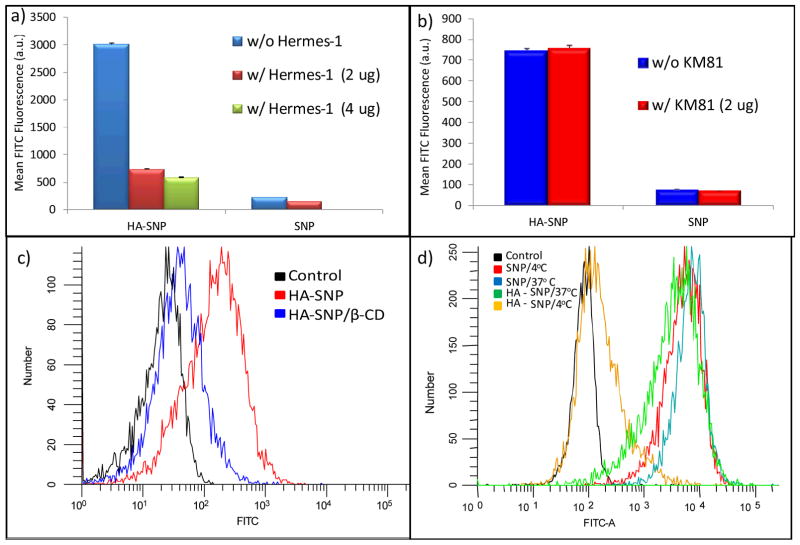
Figure 6.
Flow cytometry histograms showing the binding of SNP and HA-SNP to CD44 expressing SKOV-3 cells in the absence and presence of (a) the antiCD44 mAb Hermes-1 or (b) the isotype matched KM81. Hermes-1 led to 80% reduction in HA-SNP but not SNP binding to SKOV-3 cells. On the other hand, KM81 had no effect on the binding of either SNP or HA-SNP. (c) Flow cytometry showing the effect of β-CD on the uptake of HA-SNP. Pre-treating the cells with β-CD reduced the uptake of HA-SNP by 85% demonstrating that uptake of HA-SNP by SKOV-3 cells was mediated through cholesterol rich lipid rafts. (d) Flow cytometry showing the relative binding/uptake of HA-SNP and SNP by SKOV-3 cells at 37 °C compared to those at 4 °C. The binding/uptake of HA-SNP, but not SNP, was energy dependent. For this experiment, higher concentration of SNP than HA-SNP was used for cellular incubation due to the low uptake of SNP.