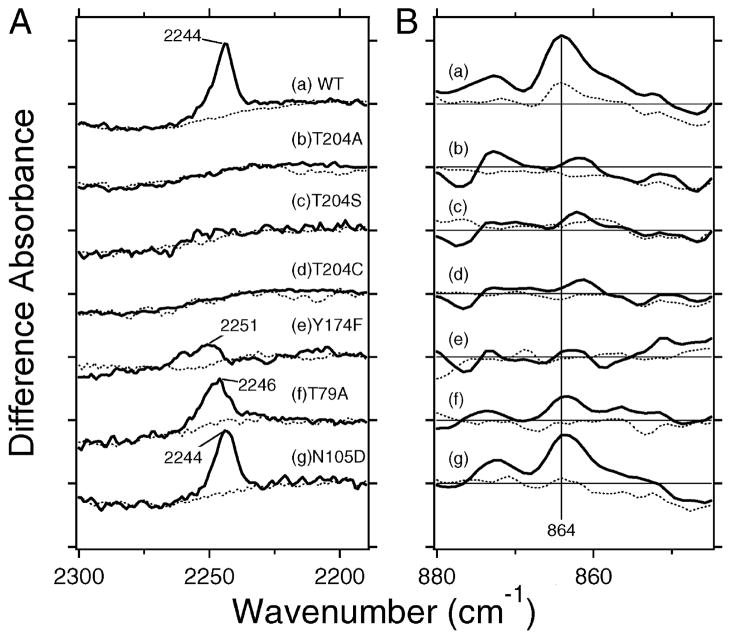
Figure 2.
(A) SRIIK minus SRII difference spectra of the wild type (a), T204A (b), T204S (c), T204C (d), Y174F (e), T79A (f), and N105D (g) in the 2330–2190 cm−1 region. The solid line represents the spectrum for the C14D-labeled retinal, while the dotted line corresponds to that for the unlabeled retinal. Vertical amplitudes of all spectra are normalized by the bands of Asn105 at 1704 (−)/1700 (+) cm−1 for spectra a–f. On the other hand, those in spectrum g were normalized to the wild type (a) by the C–C stretch at 1204 (−) cm−1 (unlabeled retinal) or the bands at 1743 (−)/1738 (+) cm−1 (C14D-labeled retinal) (see Figure S1 in detail). One division of the y-axis corresponds to 0.00018 absorbance unit. (B) SRIIK minus sRII difference spectra of the wild type (a), T204A (b), T204S (c), T204C (d), Y174F (e), T79A (f), and N105D (g) in the 880–845 cm−1 region. The solid line represents the spectrum for the unlabeled retinal, while the dotted line corresponds to that for the C14D-labeled retinal. One division of the y-axis corresponds to 0.0008 absorbance unit.