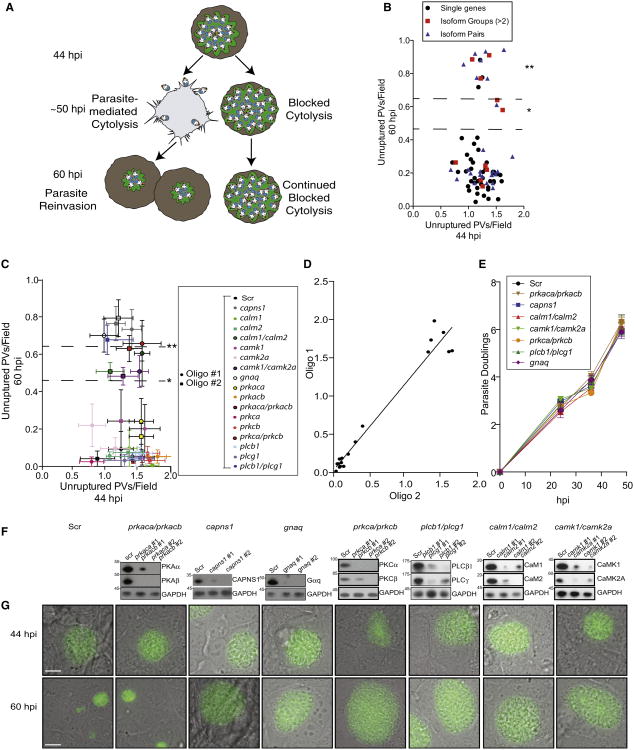
Figure 1. siRNA Screen Identifies Signaling Components Required for T. gondii-Mediated Cytolysis.
(A) Model of host siRNA screen for mediators of parasite-induced cytolysis. Defects in T. gondii-mediated cytolysis are scored at 60 hpi. Parasites unable to exit persist as vacuoles with >64 parasites, while parasites able to exit host cells reinvade new cells.
(B) Primary siRNA screen in U2OS cells. Unruptured vacuoles (intact vacuoles with >64 parasites) are compared at 44 and 60 hpi to identify host gene involvement in parasite release (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). Data shown are mean unruptured vacuoles per field ± SEM.
(C) Secondary screen utilizing multiple oligos validates individual host genes and gene pairs whose knockdown resulted in accumulation of unruptured vacuoles by 60 hpi. Data shown are mean unruptured vacuoles per field ± SEM.
(D) Pearson correlation graph indicates strong relation between siRNA oligos (r = 0.91).
(E) Measurements of parasite doublings within stable shRNA knockdown cell lines.
(F) Western blot analysis confirms shRNA-mediated stable knockdown of target proteins, as compared to Scr oligo.
(G) Representative images of P30-GFP vacuoles in stable knockdown cell lines at 44 and 60 hpi. Also see Figure S1 and Table S1.