Figure 2.
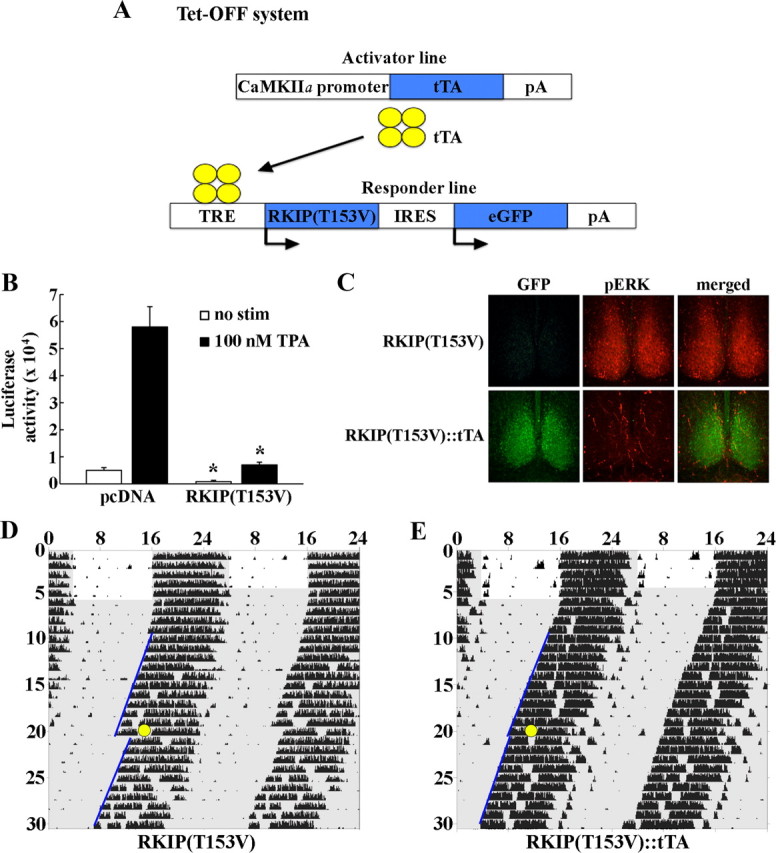
Phosphorylation of RKIP at Thr-153 mediates stimulus-dependent MAPK/ERK activation and light-induced phase shifts in circadian locomotor rhythms. A, Schematic diagram of the tetracycline-inducible system used to drive expression of dominant-negative RKIP in the murine forebrain. A single transgenic construct carrying two genes, dominant-negative RKIP harboring the T153V mutation and eGFP, in a polycistronic unit under the control of the tetracycline-responsive (TRE) promoter was generated. RKIP(T153V)-IRES-eGFP transgenic mice (hereafter referred to as RKIP[T153] single transgenics) were bred with the CaMKIIα-tTA mice. In the absence of the tetracycline analog doxycycline, double-transgenic mice coexpress RKIP(T153V) and eGFP in CaMKIIα-expressing cells. B, Neuro2A cells were transfected with an E1B-luciferase reporter gene construct and the Gal4-Elk1 expression vector, in combination with the pcDNA3.1-RKIP(T153V) expression construct or pcDNA empty vector control. Twenty-four hours post-transfection, cultures were treated with 100 nm TPA and assayed 6 h later. Basal (no stimulus) and TPA-induced Gal4-Elk1 activation were markedly attenuated in cells overexpressing dominant-negative RKIP compared with pcDNA controls. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of quadruplicate determinations. *p < 0.05 vs pcDNA control. C, Overexpression of dominant-negative RKIP in the SCN blocks light-induced ERK1/2 activation. Single-transgenic RKIP(T153V) (top) and double-transgenic RKIP(T153V)::tTA (bottom) mice received a 15 min light pulse (30 lux light intensity) at CT 15 and were killed 15 min later. SCN tissues were probed with antibodies against GFP (green) or phospho-p44/p42 MAP kinase (Thr202/Tyr204) (red). Light triggers robust phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in the SCN of single-transgenic mice, but not in double-transgenic mice expressing a nonphosphorylatable form of RKIP. D, E, Overexpression of dominant-negative RKIP in the SCN attenuates light-induced phase delays in circadian locomotor rhythms. Representative double-plotted activity profiles of single-transgenic RKIP(T153V) (D) and double-transgenic RKIP(T153V)::tTA (E) mice that were stably entrained in a fixed 12:12 LD cycle before release into constant darkness (DD). After 2 weeks in DD, mice received a 15 min light pulse (30 lux intensity: yellow circle) at CT 15 and returned to DD for an additional 2 weeks. Periods of darkness are shaded in gray. Activity onsets are indicated by blue lines. y-axis indicates the nth day of study. x-axis indicates time in hours. Double-transgenic RKIP(T153V)::tTA mice showed a statistically significant reduction in light-induced phase delays compared with single-transgenic controls.
