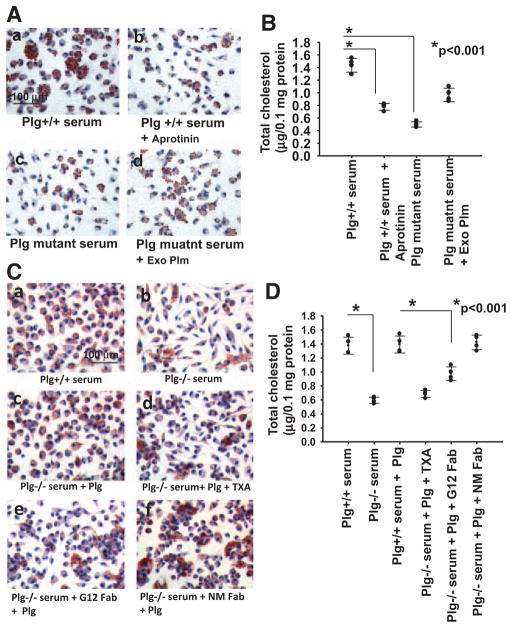
Figure 2.
Plasminogen (Plg) receptors and plasmin activity are required for Plg-mediated foam cell formation. A and B, Thioglycollate-elicited macrophages from Plg+/+ mice were untreated or treated with aprotinin (100 KIU/mL). The cells were then allowed to form foam cells by adding oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL) in the presence of serum derived from Plg+/+ mice or Plg mutant mice (expressing active-site mutant of Plg). C and D, Tranexamic acid (TXA; 200 μmol/L), Fab fragments of anti-H2B monoclonal antibody (G12; 8 μmol/L), nonimmune mouse IgG Fab (NM; 8 μmol/L), or buffer was added to thioglycollate-elicited macrophages, and foam cell formation was induced with OxLDL. A and C, Oil Red O staining of foam cells at original ×40 magnification. Images are representative of 2 independent experiments. B and D, Total cholesterol was measured in the cultured macrophages. Each dot is 1 of 4 replicates; error bars are ±SD of the mean. Exo Plm indicates exogenous plasmin.