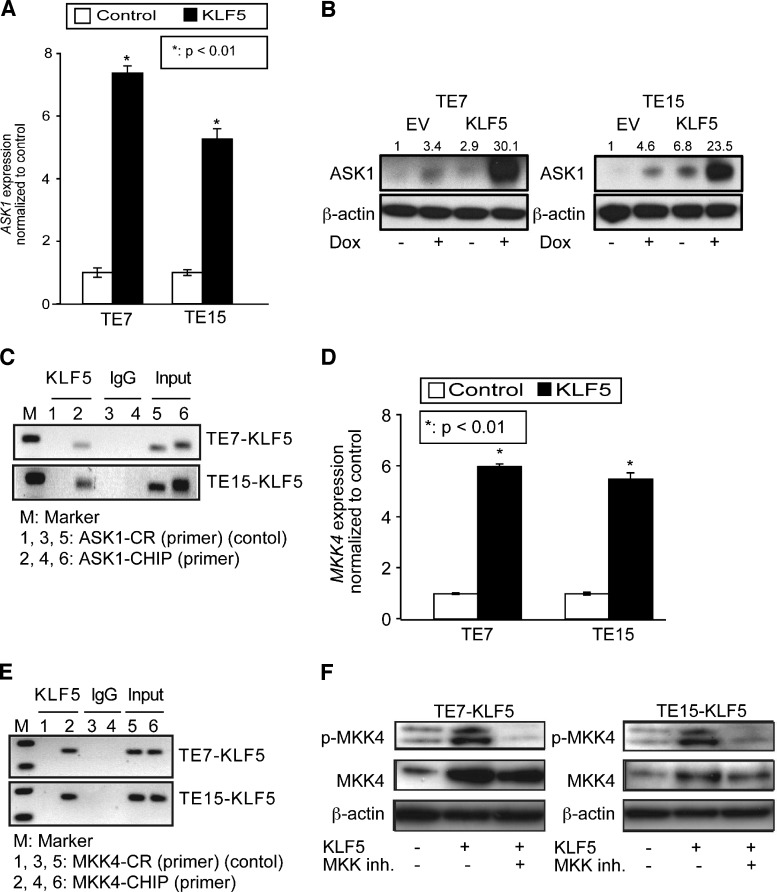
Figure 4.
KLF5 upregulates upstream mediators of the JNK pathway. (A and B) When KLF5 was induced for 24 hours in TE7 and TE15 ESCC cells, levels of ASK1 mRNA (A) and protein (B) increased. (C) ChIP assays demonstrated KLF5 binding to the 5′ regulatory region of ASK1, in the vicinity of a predicted KLF5 binding site. IgG was a negative control, and input DNA served as a positive control. ASK1 ChIP primers spanned the region from -502 to -280 upstream of the translation start site and control primers spanned the region from -1833 to -1653. (D) By qPCR, KLF5 induction for 24 hours in ESCC cells resulted in a six-fold increase in MKK4 mRNA expression as demonstrated by qPCR. (E) KLF5 bound to a region on MKK4 predicted to contain multiple KLF5 binding sites. IgG and input DNA served as controls. Primers for MKK4 ChIP and control spanned the regions -226 to +4 and -1436 to -1266, respectively, upstream of the translation start site. (F) As seen on Western blot, MKK phosphorylation was increased following KLF5 induction for 24 hours; this increase was blocked by treatment with the MAP2K inhibitor PD98059. Note that total MKK4 is also increased by KLF5 induction, indicative of both transcriptional and posttranslational regulation of MKK4.