Fig. 2.
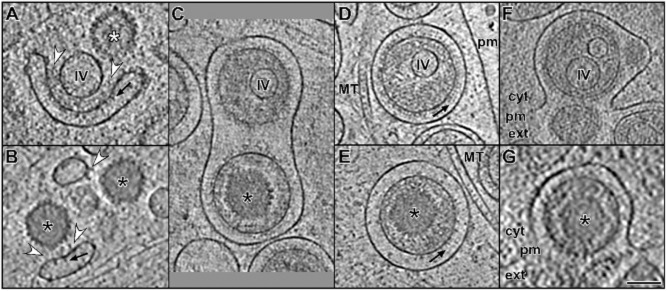
Structural comparison between L-particle and virion assembly and egress in cryo-ET. Slices through tomographic volumes showing secondary envelopment and exit of HSV1 L-particles (upper row) and virions (lower row).
A and B. At axon terminals, membranous compartments associated with glycoproteins (black arrows) and tegument (white arrowheads) surround inclusion vesicles (IV) and capsids (black and white asterisks for C- and B-capsids respectively). (B) is a zoom into fig. 6C from Ibiricu et al. (2011).
C. L-particle and virion sharing a membranous compartment in an axon terminal. Black arrows: glycoproteins; MT: microtubule; pm: plasma membrane; black asterisk: C-capsid.
D and E. L-particle and virion from the same tomogram in a middle region of an axon.
F and G. Exit by fusion of the membranous compartment with the plasma membrane (pm) at an axon terminal. Black asterisk: C-capsid; cyt: cytoplasm; ext: extracellular space; MT: microtubule; pm: plasma membrane.
Scale bar for (A)–(G): 100 nm.
