Figure 3.
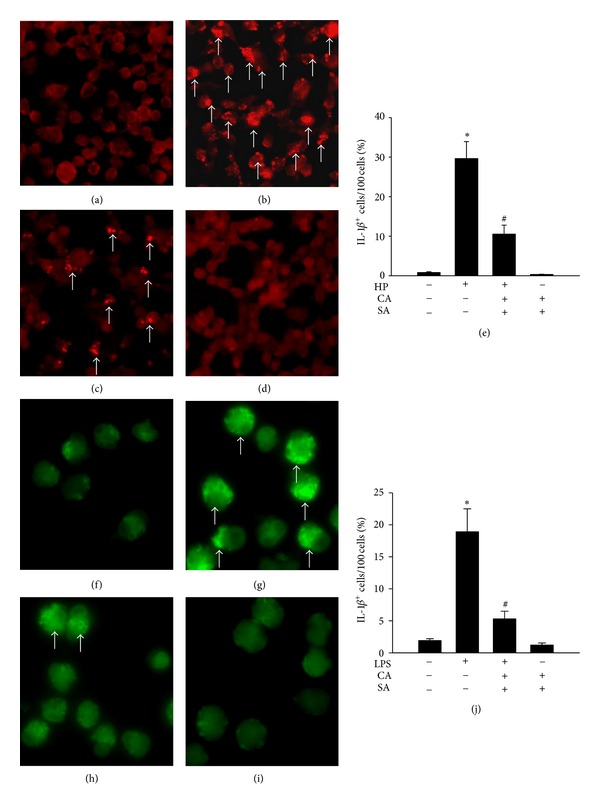
Effects of catechins (CAs) and/or sialic acid (SA) on IL-1β expression measured by immunofluorescence staining in AGS cells at 4 h after infection with H. pylori (HP) ((a–e), ×200 magnification) or LPS ((f–j), ×400 magnification). Arrows indicate IL-1β-positive stains (bright red and bright green). (a, f) Control AGS cells; (b) H. pylori-infected AGS cells; (c) CASA-treated H. pylori-infected AGS cells; (g) LPS-treated AGS cells; (h) CASA-treated LPS-treated AGS cells; (d, i) CASA-treated control AGS cells; and (e, j) IL-1β immunofluorescence staining results analyzed using Image-J software. Data show changes in the percentage of IL-1β-positive cells, compared to the untreated uninfected control, which was set at 1.0. Each column with a vertical line represents mean ± SEM (n = 4). *P < 0.05, compared to the untreated uninfected control; # P < 0.05, compared to H. pylori infection or LPS treatment alone.
