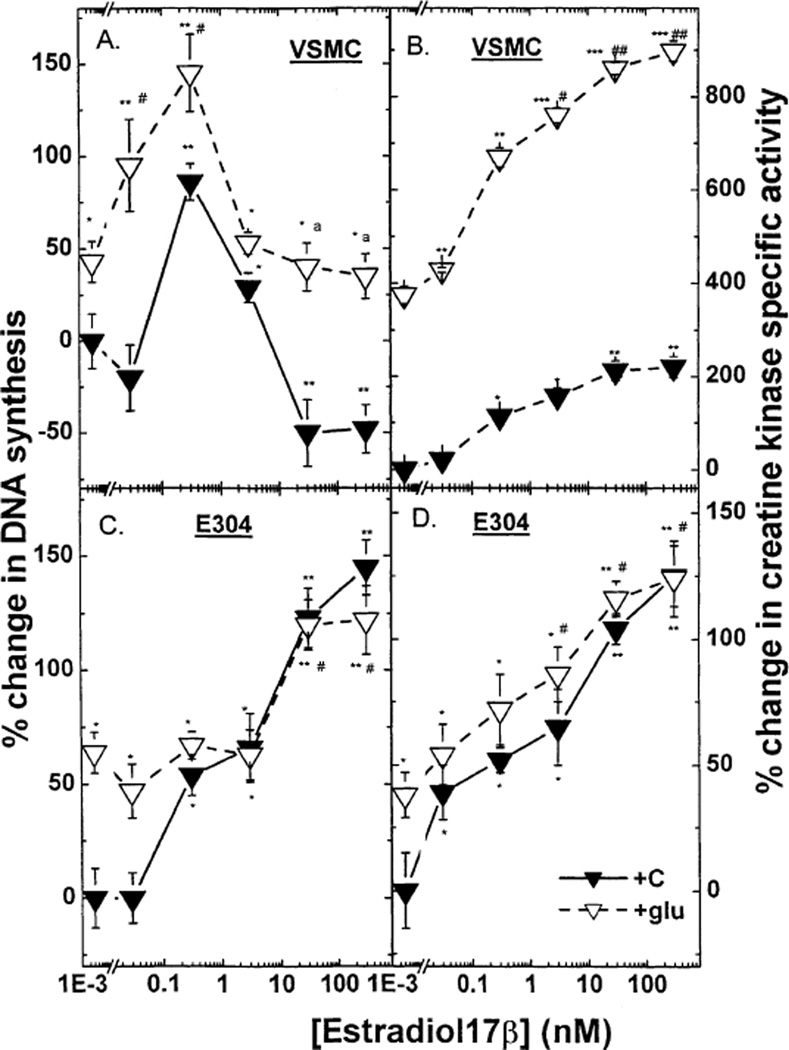
Fig. 1.
The effect of estradiol 17β (0.03–300 nM) in the presence or absence of high glucose on 3[H] thymidine incorporation in VSMC (A), E304 cells (C), and on creatine kinase specific activity in VSMC (B) and E304 cells (D). Cells were prepared, grown and hormonally treated as described in the experimental section. Results are means ±S.E.M. of 4–12 incubates from 2 to 4 experiments and are expressed as the ratio between 3[H] thymidine incorporation or as the ratio between enzyme activity in hormone-treated and control (without hormone) cells. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 for the comparison with control values at low glucose; and # P < 0.05 and ## P < 0.01 for the comparison with control values at high glucose; a P < 0.05 for the comparison between the effect of E2 with and without glucose. The statistical analysis was done by ANOVA. The basal levels of creatine kinase specific activity in VSMC and in E304 cells were 0.050 ± 0.001 and 0.116 ± 0.017 µmol/min/mg protein respectively. The basal levels of 3[H] thymidine incorporation into DNA in VSMC and in E304 cells were 7200 ± 1080 and 94100 ± 12233 dpm per well, respectively.