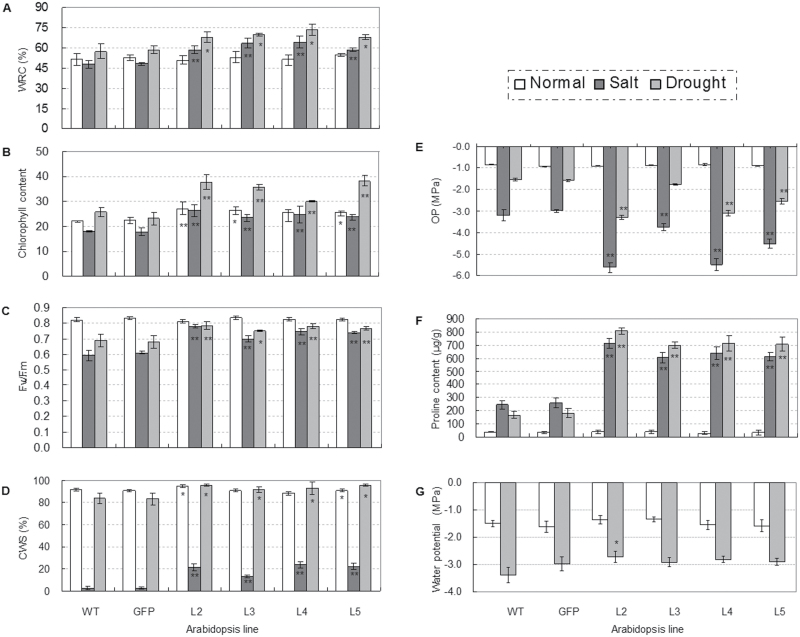
Fig. 6.
Comparisons of physiological indices related to abiotic stress responses for TaSnRK2.3 plants under stress or no-stress conditions. (A–F) TaSnRK2.3 transgenics had a higher water retention ability (WRA) (A), chlorophyll content (B), photosynthetic potential (C), cell membrane stability (CMS) (D), proline content (E), and water potential (F) under drought and/or salt stress conditions. * and ** indicate significant differences at P <0.05 and P <0.01, respectively. WT, wild type; GFP, GFP transgenic line; L2–L5, four TaSnRK2.3 transgenic lines. The values are means ±SE. For (A–C), n=10, n=20, and n=40, and for (E) and (F), n=3. (G) Transgenic TaSnRK2.3 plants had lower osmotic potential (OP). Four TaSnRK2.3 transgenic lines, as well as the WT and GFP plants, cultured under well-watered conditions, were subjected to OP assays. Five plants of each line were collected as a sample; three replications were set for each line. The values are means ±SE (n=3).