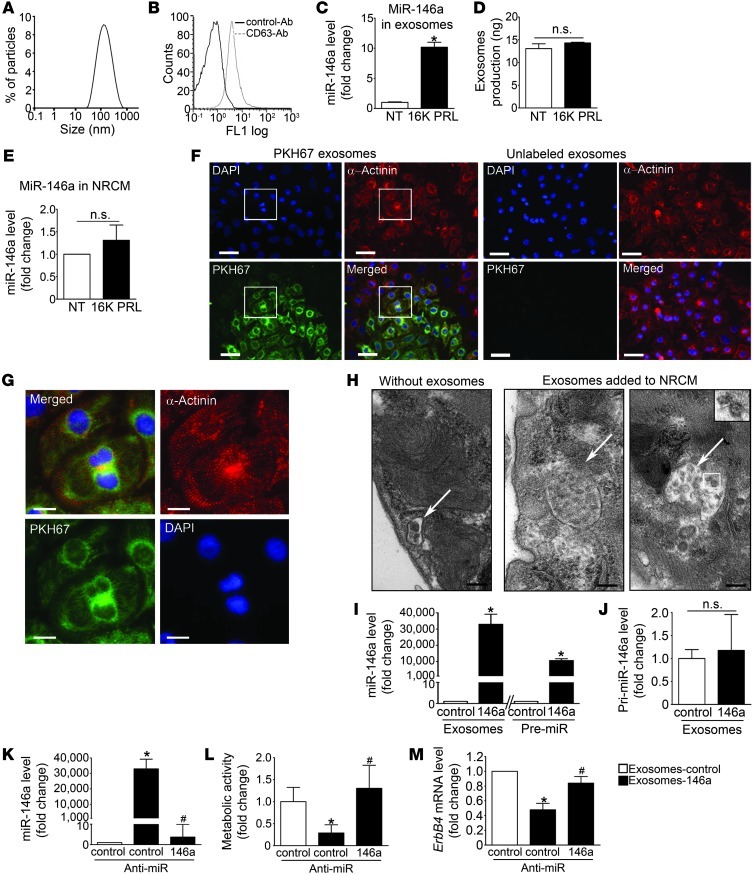
Figure 3. miR-146a can be exported from ECs in exosomes that can be transferred to cardiomyocytes and impair their metabolism.
(A) Dynamic light scattering analysis of conditioned medium of 16K PRL–treated HUVECs (50 nM, 24 hours). (B) Flow cytometry analysis of exosomes purified from HUVEC medium and labeled with CD63. (C) miR-146a level in exosomes from HUVECs treated with 16K PRL or not treated (NT). (D) Exosome production by HUVECs treated or not with 16K PRL (50 nM, 48 hours). (E) miR-146a level in NRCMs treated or not with 16K PRL. (F) Fluorescence microscopy detecting fusion of miR-146a–loaded endothelial exosomes labeled with the green fluorescent PHK67 membrane linker with NRCMs (α-actinin, red; DAPI, blue). Scale bars: 50 μm. (G) Higher-magnification views of boxed regions in F. Scale bars: 15 μm. (H) Electron micrographs of NRCM sections showing vesicles (arrows); after a 16-hour incubation with HUVEC exosomes, NRCMs showed larger multivesicular vesicles containing the exosomes (inset; enlarged ×2-fold). Scale bars: 500 nm. (I) miR-146a level in NRCMs exposed to miR-146a-exosomes or control-exosomes or transfected with pre-miR-146a or pre-miR-control. (J) Expression level of pri-miR-146a in NRCMs exposed to miR-146a- or control-exosomes. (K) miR-146a expression level, (L) metabolic activity, assessed by MTS assay, and (M) Erbb4 level in NRCMs exposed to control exosomes, miR-146a exosomes, and miR-146a exosomes cotransfected with anti-miR-control or anti-miR-146a. All data are mean ± SD (n ≥ 3). *P < 0.05 vs. respective control; #P < 0.05 vs. miR-146a-exosomes with anti-miR-control. See also Supplemental Figure 3.