FIGURE 2:
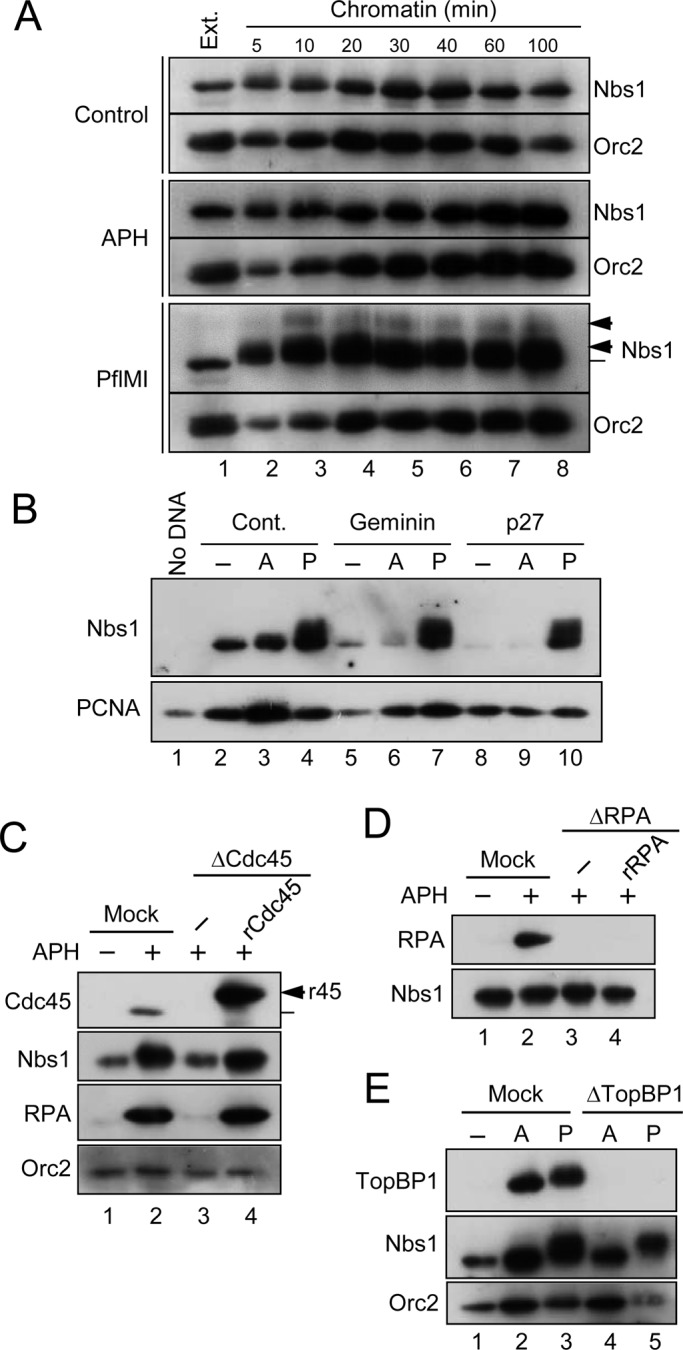
The MRN complex associates with chromatin in a replication-dependent manner. (A) Time course for binding of Nbs1 to chromatin. Interphase egg extracts treated with control buffer (top), APH (middle), or PflMI (bottom) were incubated with sperm chromatin (lanes 2–8). Chromatin fractions were prepared at the indicated times for immunoblotting with anti-Nbs1 and anti-Orc2 antibodies. Lane 1 depicts 1 μl of egg extract. (B) Extracts incubated with no checkpoint inducer (lanes 2, 5, and 8), APH (A; lanes 3, 6, and 9), or PflMI (P; lanes 4, 7, and 10) were treated with control buffer (lanes 2–4), Geminin (lanes 5–7), or p27 (lanes 8–10). Chromatin fractions were prepared and immunoblotted for Nbs1 (top) and PCNA (bottom). The sample for lane 1 lacked any added sperm chromatin. (C) Chromatin fractions were prepared from mock-treated (lanes 1 and 2) or Cdc45-depleted (lanes 3 and 4) extracts that had been incubated in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lanes 2–4) of APH. Recombinant Xenopus Cdc45 (r45) was added back in lane 4 (arrow). Samples were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. (D) Chromatin fractions were prepared from mock-treated (lanes 1 and 2) or RPA-depleted (lanes 3 and 4) extracts that had been incubated in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lanes 2–4) of APH. Recombinant human RPA (rRPA) was added to the extract in lane 4. Samples were immunoblotted with antibodies against Xenopus Nbs1 and RPA70. Note that human RPA70 does not cross-react with the anti-Xenopus antibodies. (E) Chromatin fractions were prepared from mock-treated (lanes 1–3) or TopBP1-depleted (lanes 4–5) extracts that had been incubated in the absence (lane 1) or presence of either APH (A; lanes 2 and 4) or PflMI (P; lanes 3 and 5). Fractions were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins.
