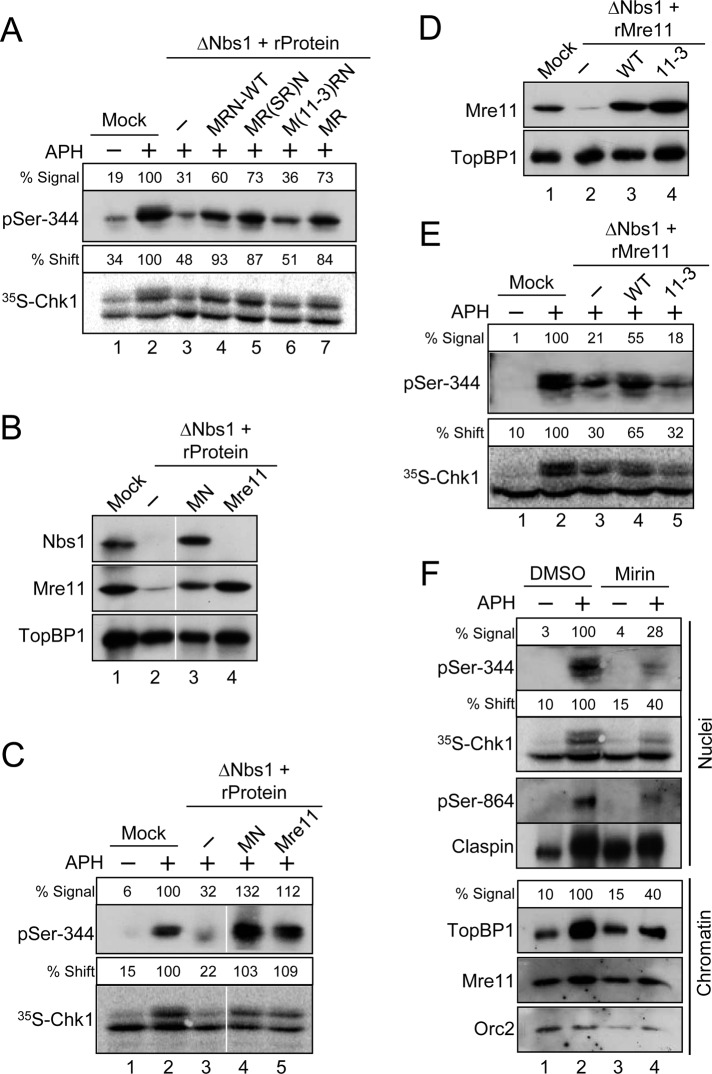
FIGURE 5:
Mre11 is essential for the DNA replication checkpoint in egg extracts. (A) Mock-depleted (lanes 1 and 2) or Nbs1-depleted (lanes 3–7) extracts were supplemented with the following: control buffer (lanes 1–3), recombinant MRN complexes containing all wild-type subunits (lane 4), a Rad50-SR mutant subunit (lane 5), or an Mre11-3 mutant subunit (lane 6), and dimeric MR complex (lane 7). Extracts were incubated with [35S]Chk1 in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lanes 2–7) of APH. Nuclear fractions from the extracts were processed for immunoblotting with anti–pSer-344 Chk1 antibodies (top) or for phosphorimaging to detect radiolabeled Chk1 (bottom). Numbers above each lane denote quantitation of phosphorylation relative to mock-depleted, APH-treated extracts. (B) Mock-treated (lane 1) or Nbs1-depleted extracts (lanes 2–4) were supplemented with control buffer (lanes 1 and 2), recombinant Mre11-Nbs1 complex (MN, lane 3) or recombinant Mre11 protein (lane 4). Extracts were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. (C) Extracts from (B) were incubated with [35S]Chk1 in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lanes 2–5) of APH. Nuclear fractions from the extracts were processed for immunoblotting with anti–pSer-344 Chk1 antibodies (top) or for phosphorimaging to detect radiolabeled Chk1 (bottom). (D) Mock-treated (lane 1) or Nbs1-depleted (lanes 2–4) extracts were supplemented with control buffer (lanes 1 and 2), recombinant wild-type Mre11 protein (lane 3), or the mutant Mre11-3 protein (lane 4). Extracts were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. (E) Extracts from (D) were incubated with [35S]Chk1 in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lanes 2–5) of APH. Nuclear fractions from the extracts were processed for immunoblotting with anti–pSer-344 Chk1 antibodies (top) or for phosphorimaging to detect radiolabeled Chk1 (bottom). (F) Effects of mirin on the DNA replication checkpoint. Egg extracts were preincubated for 20 min in the absence (lanes 1 and 2) or presence (lanes 3 and 4) of 0.8 mM mirin. At this point, extracts were supplemented with sperm chromatin and [35S]Chk1 and incubated in the absence (lanes 1 and 3) or presence (lanes 2 and 4) of APH. Nuclear fractions (top four panels) were prepared and processed for phosphorimaging and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Numbers above the lanes containing Chk1 denote phosphorylation relative to APH-containing extracts treated with DMSO. Chromatin fractions (bottom three panels) were prepared and immunoblotted for TopBP1, Mre11, and Orc2. The numbers above the lanes containing TopBP1 represent the binding of TopBP1 to chromatin relative to APH-containing extracts treated with DMSO.