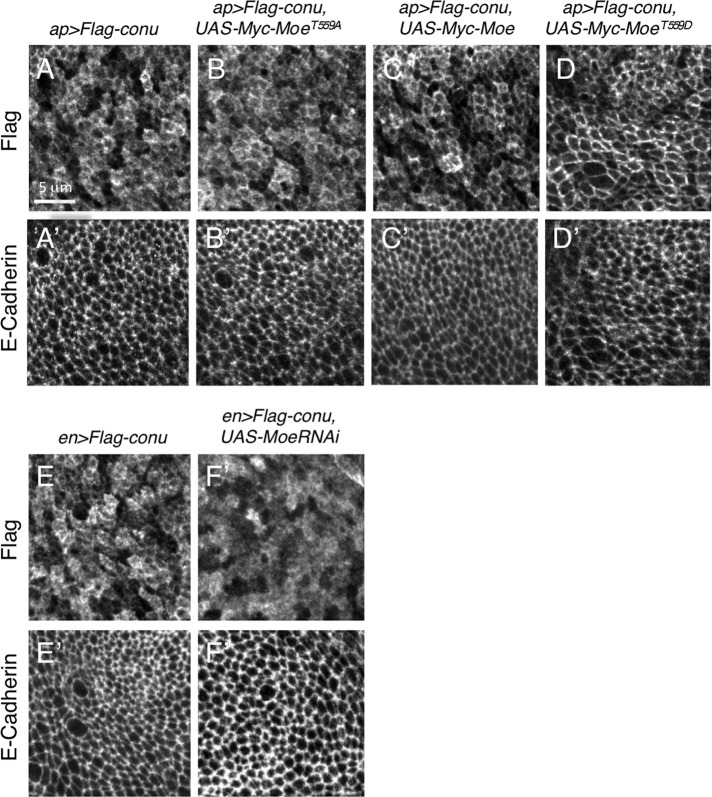
FIGURE 2:
Moe recruits Conu to the cortex, and cortical localization of Conu is dependent on Moe. (A) An epitope-tagged version of Conu has a primarily cortical localization in the wing imaginal epithelium when expressed under the apGal4 driver. (B) An unphosphorylatable form (T559A) of Moe coexpressed with Conu has no obvious effect on its localization. (C) Coexpression of wild-type Moe resulted in more cortically localized Conu. (D) Coexpression of a phosphomimetic form (T559D) of Moe resulted in a strikingly stronger cortical localization of Conu. (E) Under the enGal4 driver, epitope-tagged Conu has a primarily cortical localization, while depletion of Moe by RNAi disrupted this localization (F). E-cadherin, an adherens junction protein, is shown for all images to show that the plane of section cuts through the junctional region (A′ –F′). Scale bar in (A) represents 5 μm in all panels.