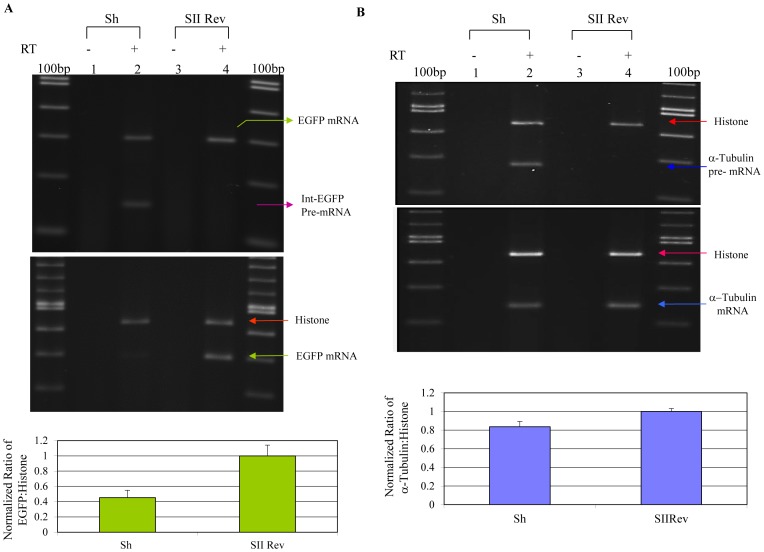
Figure 7. RT-PCR detection of EGFP pre-mRNA.
A) (Upper panel) Lanes 2 and 4 illustrate detection of EGFP mRNA (upper band) and pre-mRNA (lower band) in RNA samples isolated from anti-U5-200kD shRNA and irrelevant shRNA treated cells, respectively. Lanes 1 and 3 are minus RT controls. (Middle panel) RT-PCR analysis of EGFP mRNA expression. Lanes two and four demonstrate expression of the histone (top band) and spliced EGFP mRNAs in anti-U5-200kD shRNA and irrelevant anti-EGFP rev shRNA treated 293/EcR cells. Lanes 1 and 3 are minus RT reactions. (Lower panel) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the EGFP mRNA expression. B) RT-PCR detection of alpha-tubulin pre-mRNA and histone mRNA. (Upper panel) The lower band in Lane 2 is the alpha-tubulin pre-mRNA product from samples treated with U5-200kD specific shRNA and the irrelevant anti-Rev shRNA, respectively. The upper bands are the histone products used for normalization. Lanes 1 and 3 are minus RT controls. The 100bp size marker was used for product size verification. (Middle panel) RT-PCR detection of the alpha-tubulin and histone mRNAs. The lower bands in Lanes 2 and 4 are alpha-tubulin products from samples treated with the U5-200kD specific hairpin and the irrelevant anti-Rev shRNAs, respectively. The upper bands are the histone products used for normalization. Lanes 1 and 3 are minus RT controls. The 100bp size marker was used for product size verification. (Lower panel) Semi-quantitative analysis of alpha-tubulin mRNA expression. Semi-quantitative analysis of alpha-tubulin mRNA expression normalized against histone mRNA expression revealed only a 16% reduction in the expression of the alpha-tubulin mRNA in the splicing defect background.