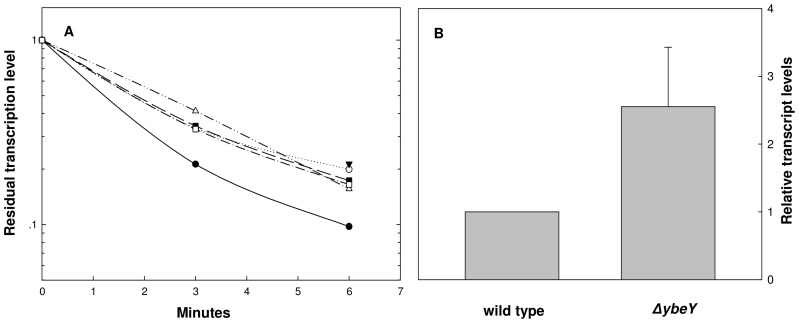
Figure 2. Stability and levels of RNA expressed from various rrn promoter regions in ybeY deletion mutant.
(A) Stability of lacZ gene transcripts was determined by measuring its residual levels following addition of Rifampicin (200 µg/ml). Cultures and growth conditions were as described in Figure 1. All the bacteria were deleted for the chromosomal lacZ gene and transformed with pACYC plasmids carrying various rrn promoter sequences fused upstream to a promoterless lacZ. The plasmids carried the “S” region, “M” region, or “L” region. Rifampicin was added at time 0 and the cultures were harvested at 0, 3, 6 min. RNA was extracted and analyzed by qRTPCR. Bacteria with wild type ybeY gene and plasmid with “S” region (filled circles), with “M” region (open circles) and with “L” region (filled triangles). ΔybeY mutant carrying a plasmid with “S” region (open triangles), with “M” region (filled squares) and with “L” region (opened squares). (B) Levels of RNA encoded from the region prior to the antitermination sequences. Cultures of wild type and ΔybeY mutant were grown in LB at 37°C and harvested at O.D600 = 0.45. RNA was extracted from these samples and the levels of the transcripts encoded by the region before the antitermination sequences were quantified by qRTPCR from the primers described above.