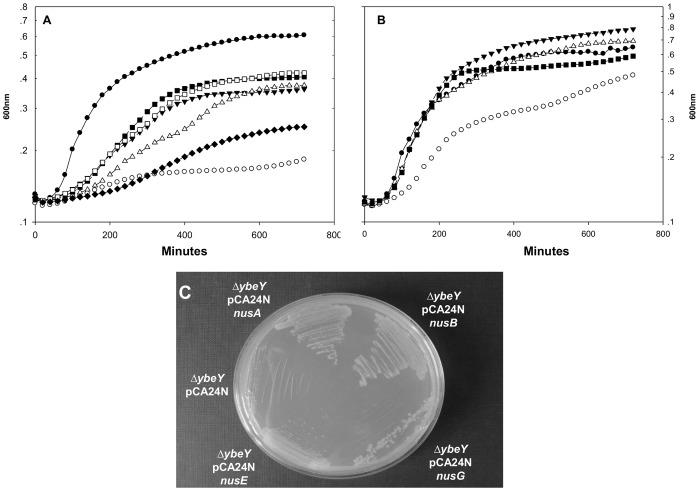
Figure 3. Effect of plasmids expressing transcriptional antitermination factors on growth of ybeY deletion mutant.
Over-expression of NusA, NusB, NusG and NusE, was obtained by introducing multi-copy plasmids containing these genes cloned downstream to a lacZ promoter. These plasmids were transformed into the ybeY deletion mutant (A) and into the wild type strain (B). Cultures were grown overnight in LB medium at 30°C. They were then diluted to A600 of 0.04 in 2 ml wells (in a 24 well plate) containing 1 ml of LB medium supplemented with 0.1 mM IPTG for inducing the lacZ promoter. The cultures were transferred to 42°C and turbidity was measured at 600 nm for 12 hours. (A) wild type (filled circles), ybeY deletion mutant (open circles), ΔybeY mutant carrying pCA24N nusA (filled triangles), ΔybeY mutant carrying pCA24N nusB (open triangles), ΔybeY mutant carrying pCA24N nusE (filled squares), ΔybeY mutant carrying pCA24N nusG (opened squares) and ΔybeY mutant carrying pCA24N empty vector (filled diamonds). (B) wild type (filled circles), wild type carrying pCA24N nusA (open circles), wild type carrying pCA24N nusB (filled triangles), wild type carrying pCA24N nusE (open triangles) and wild type carrying pCA24N nusG (filled squares). (C) Growth of ΔybeY mutant carrying pCA24N encoding Nus genes on LB agar plates, supplemented with 0.1 mM IPTG, overnight at 42°C.