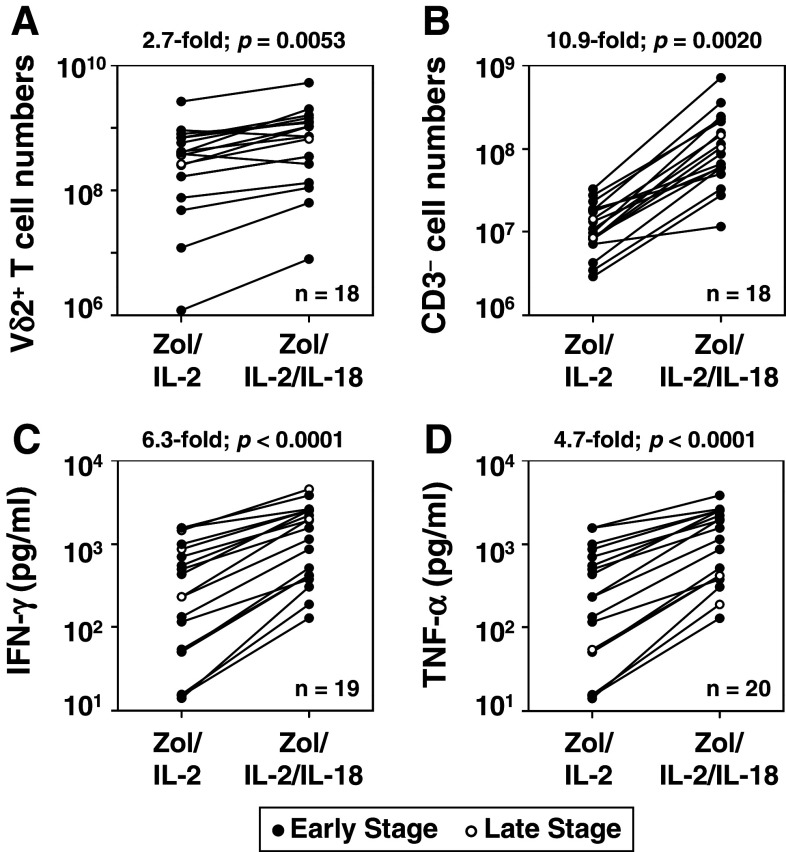
Fig. 4.
IL-18 augments expansion of Vδ2+ T cells and CD3− “helper” NK cells and the effector functions of Vδ2+ T cells. a, b Effect of IL-18 on the expansion of Vδ2+ T cells (a) and CD3− “helper” NK cells (b). PBMC derived from 18 breast cancer patients were stimulated with Zol/IL-2 or Zol/IL-2/IL-18 for 10 days, and the numbers of Vδ2+ T cells and CD3− “helper” NK cells determined by vital dye exclusion and flow cytometry. Each line connects the cell numbers after expansion by Zol/IL-2 with the cell numbers after expansion by Zol/IL-2/IL-18 from the same patient. c, d Effect of IL-18 on the production of IFN-γ (c) and TNF-α (d) by PBMC after stimulation with Zol/IL-2 or Zol/IL2/IL-18. PBMC from 19 (c) or 20 (d) breast cancer patients were stimulated with Zol/IL-2 or Zol/IL-2/IL-18 for 2 days, the culture supernatants harvested, and IFN-γ and TNF-α levels determined by ELISA. Each line connects cytokines produced in response to Zol/IL-2 or Zol/IL-2/IL-18 by PBMC from the same patient. Data obtained from early- and late-stage breast cancer patients were plotted as closed and open circles, respectively