Figure 2.
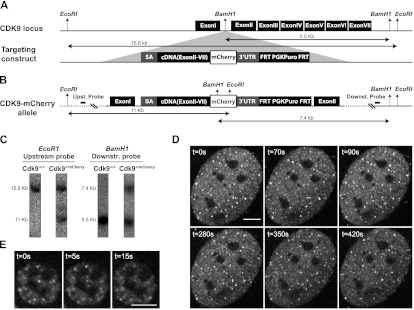
Generation of a CDK9-mCherry knock-in mouse and imaging of primary cells. (A) The CDK9 locus was targeted with a construct consisting of upstream and downstream homology arms flanking a DNA fragment that has a splice acceptor, cDNA (exon II–VII), fused in-frame to mCherry, followed by a stop codon, the 3′ untranslated region (UTR( of the Cdk9 gene, and the puromycin selection marker flanked by FRT sequences. The insert was recombined into a unique BamH1 site in the intron I of Cdk9 gene. (B) The targeted (CDK9-mCherry) allele is shown with restriction sites and the corresponding fragment sizes. Probes for Southern blot analysis are located outside the targeting arms (distances are not scaled). (WT) Wild type; (Puro) puromycin. (C) Southern blot of a correctly targeted clone. Upstream and downstream probes were hybridized with DNA digested with EcoRI and BamH1, respectively. Unprocessed in vivo images of primary MEFs (D) and fetal liver cells (E) isolated from a knock-in CDK9-mCherry mouse. The real-time unprocessed movies are shown in Supplemental Movies S2 and S3. Bar, 5 μm.
