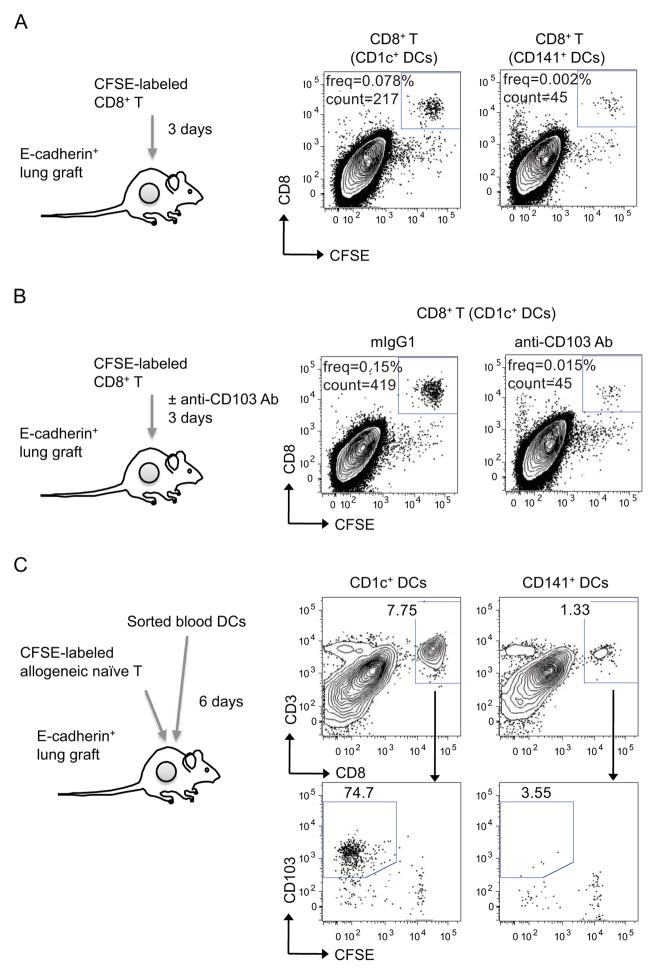
Figure 5. CD1c+ DCs elicit the differentiation of CD103+CD8+ T cells in vivo.
(A–B) CD1c+ and CD141+ DCs were purified from human blood and cocultured with allogeneic naïve CFSE labeled CD8+ T cells. Proliferating CFSE− CD8+ T cells cultured with either CD1c+ or CD141+ DCs were sorted and further labeled with CFSE. CFSE-relabeled T cells (1×105 cells) were injected into the human epithelial grafts and single-cell suspensions were analyzed by flow cytometry at day 3. Dot plots show the presence of CD8+CFSE+ T cells. (B) Anti-CD103 or isotype control Abs (50 μg) were given daily to block T cell binding. (C) CD1c+ and CD141+ DCs subsets sorted from human blood were co-injected with allogeneic naïve CFSE-labeled T cells (3×105 DCs and 3×106 T cells) into human epithelial environments. Human epithelia were harvested 6 days later and analyzed by flow cytometry. Dot plots show the presence of CD3+CD8+ human T cells (upper plots) and the percentages of CFSE-negative CD103+ cells in gated CD3+CD8+ T cells (lower plots). One of two experiments shown. See also Figure S5.