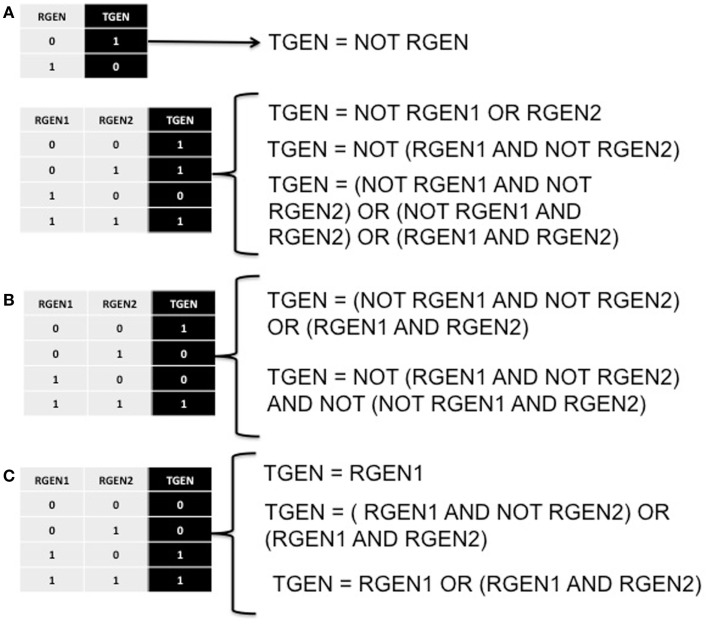
Figure A3.
Truth tables and equivalent logical statements for global negative, ambiguous, and neutral regulator definitions. (A) Two examples of a negative global regulator. As observed in the first example, the regulator can only be expressed with a NOT logical operator in the logical statement. In the example below, equivalent logical statements where RGEN1 acts as a negative and as an ambiguous regulator can be used. However, we can observe that if RGEN1 is labeled as a negative global regulator, we can always express RGEN1 in a logical statement with a NOT logical operator. (B) An example of ambiguous global regulators. In this example, the regulators can only be expressed as ambiguous regulators using a NOT logical operator in one part of the sentence and omitting the NOT operator in the other part of the sentence. (C) A neutral global regulator. The logical statement can be written without including the neutral global regulator (RGEN2). However, we can use an equivalent logical statement to include RGEN2 as a positive, negative, or neutral regulator. Neutral global regulators can always be removed from the logical statement.