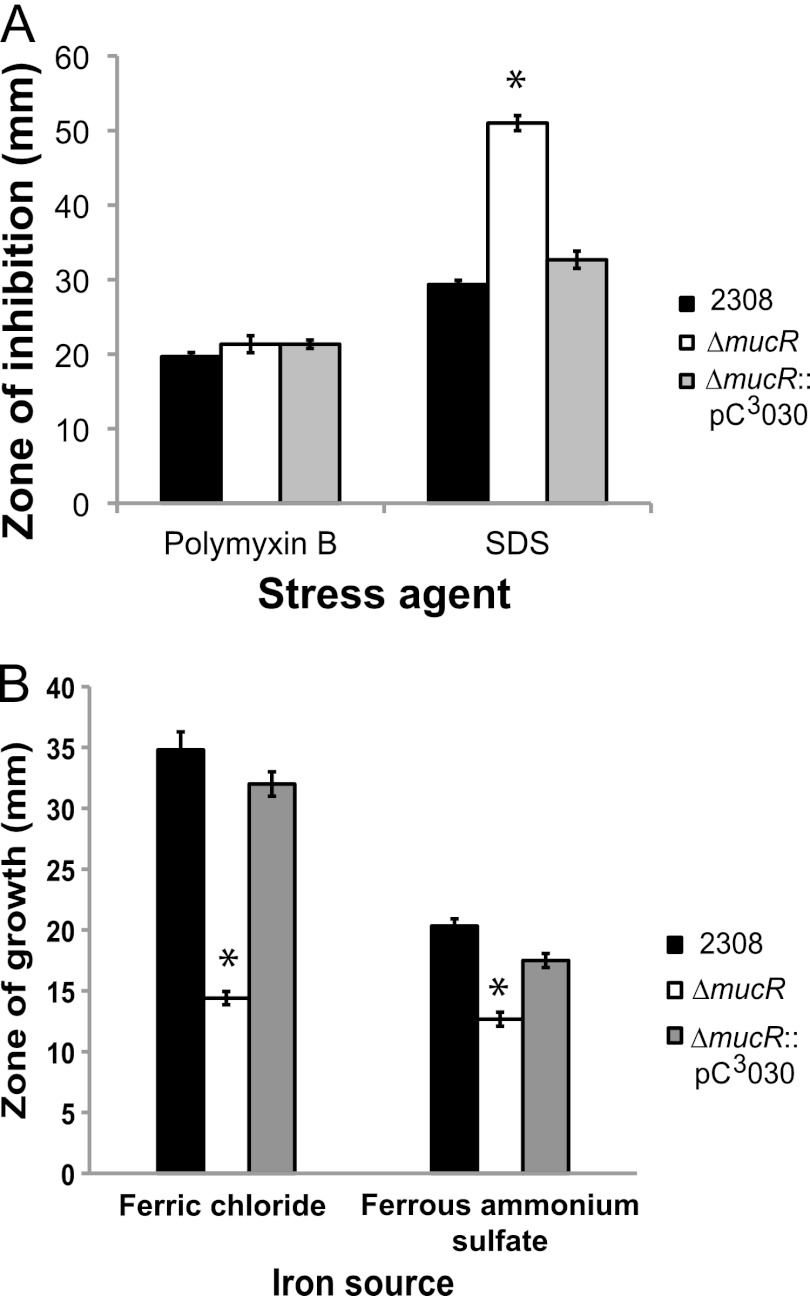
Fig 4.
The Brucella abortus mucR mutant exhibits a cell envelope defect and an iron acquisition defect in vitro. (A) Brucella strains were tested in a disk diffusion assay for their comparative susceptibilities to polymyxin B and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). The results are plotted as the average diameters (±standard deviations) of the zones of inhibition around disks containing the indicated stress agents, and the results are from single experiment that was repeated in triplicate. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences (t test; P < 0.05) between a mutant strains and parental strain 2308. (B) Brucella abortus 2308, the mucR mutant strain (ΔmucR), and the complemented mucR mutant strain (ΔmucR::pC3030) were tested for their ability to utilize ferric (Fe3+) or ferrous (Fe2+) iron in a disk diffusion assay. Iron sources (50 mM FeCl3 or 50 mM ferrous ammonium sulfate) were applied to sterile Whatman paper disks on plates containing the chelator EDDHA, and following incubation at 37°C for 72 h, the diameter (in millimeters) of the zone of bacterial growth around each filter disk was measured. The data are represented as the average and standard deviation of the zones of growth recorded for each strain in triplicate, and asterisks denote statistically significant differences (t test; P < 0.05) between the mucR mutant strain and parental strain 2308.