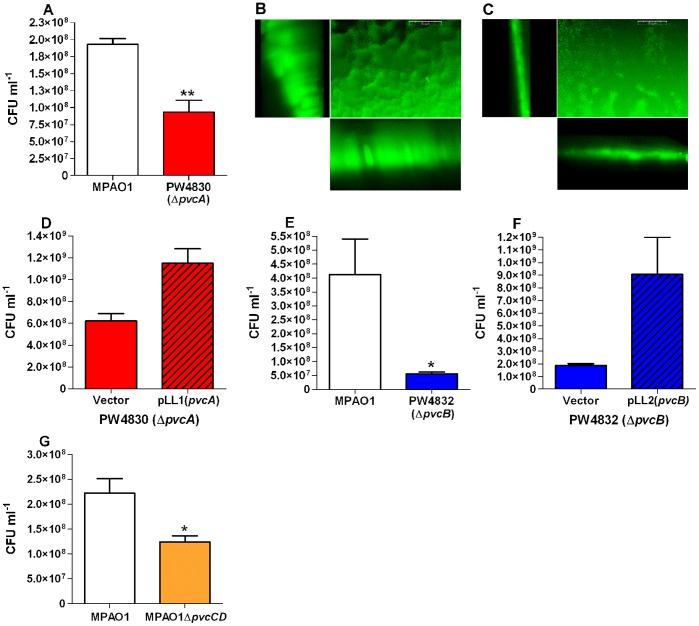
Figure 1. pvc genes affect biofilm development in MPAO1.
A. Mutation in pvcA reduces biofilm development in the MPAO1 isogenic mutant PW4830. Strains were transformed with pMRP9-1, which expresses GFP. Overnight cultures were subcultured into tryptone broth as described in Materials and Methods. Bacterial biofilms formed in a ring at the air-liquid interface were washed to remove planktonic cells and the biofilm cells were removed by vortexing in PBS, diluted tenfold, and plated to quantify the viable microorganisms within the biomass (CFU ml−1). B and C. Representative photomicrographs of the biofilms formed by (B) MPAO1 and (C) PW4830 (ΔpvcA) visualized with CLSM at 40X magnification. Z slices of 0.5 µm were generated; the zy and zx planes of the Z images are shown to the left and below the flat field, respectively. Bars equal 50 nm. D–G. Biofilms were developed and CFU assayed as described in A. D. Plasmid pLL1 carrying intact pvcA constitutively expressed from the lac promoter complements the defect of PW4830 in biofilm formation. Strains were transformed with pLL1 or pCR2.1-1.8 (vector control). E. Mutation in pvcB also reduces biofilm development in the MPAO1 isogenic mutant PW4832. F. Plasmid pLL2 carrying intact pvcB constitutively expressed from the lac promoter complements the defect of PW4832 (ΔpvcB) in biofilm formation. Strains were transformed with pLL1 or pCR2.1-1.8 (vector control). G. Mutation in pvcC-D reduces biofilm development in the MPAO1 isogenic mutant MPAO1ΔpvcC-D. Values in A and D-G represent the average of three independent experiments ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical significance in viable biomass between the strains was calculated by Student’s unpaired t-test. P<0.05 (*); P<0.01 (**).