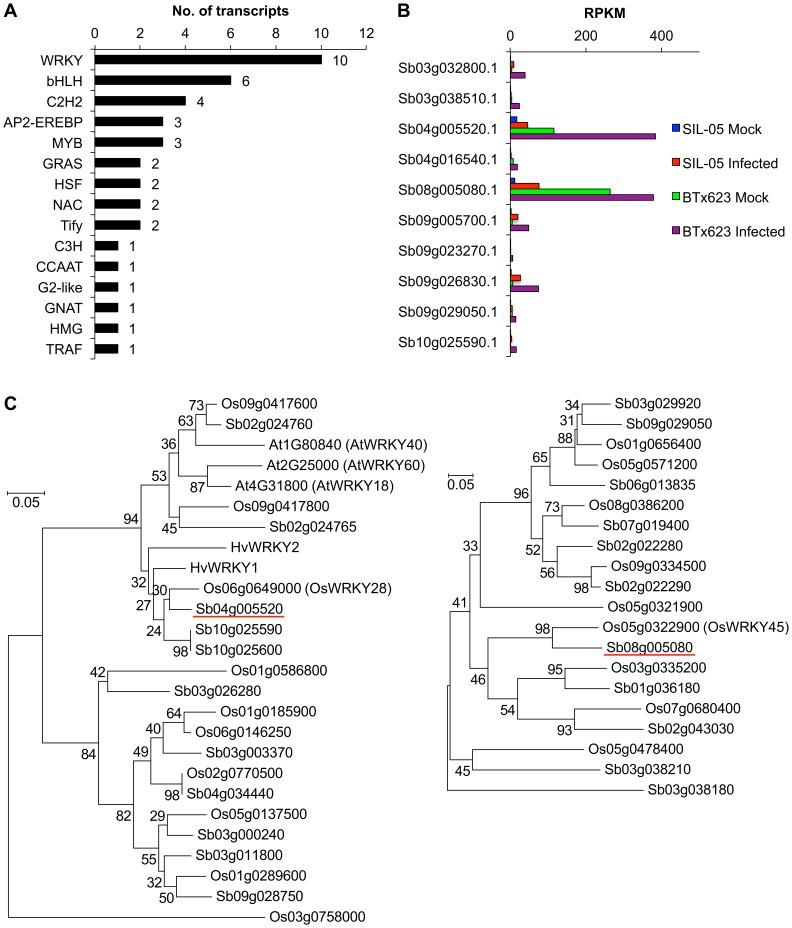
Figure 3. Pathogen (Bipolaris sorghicola)-induced genes encoding transcriptional factors in sorghum.
(A) Number of pathogen-induced transcripts for each family. Families of the transcriptional factors (TFs), shown at left, were defined on the basis of a homology search in the Plant Transcription Factor Database [22]. (B) Expression of the 10 induced WRKY TFs. RPKMs of each transcript were compared in mock- and pathogen-infected leaves by using the disease-resistant cultivar SIL-05 in the early stages of infection (24 h) (this study) and a related cultivar, BTx623, at a relatively late infection stage (7 days) (our previous study [13]) (C) Phylogenetic tree of the 2 WRKY TFs for which the genes were expressed at relatively high levels. The amino acid sequences of WRKY domain (PF03106) of Sb08g005080 (red underline in right panel) and Sb04g005520 (red underline in left panel), and their best 10 BLAST hits in the Phytozome sorghum protein database [16] and the Rice Annotation Project (RAP) protein database (http://rapdb.dna.affrc.go.jp), were aligned by using ClustalW. Phylogenetic trees were constructed by using MEGA5. For Sb04g005520, HvWRKY1/2 and ATWRKY40/60 were also aligned. Abbreviations are as follows: Sb, Sorghum bicolor; Os, Oryza sativa (rice); Hv, Hordeum vulgare; At, Arabidopsis thaliana.