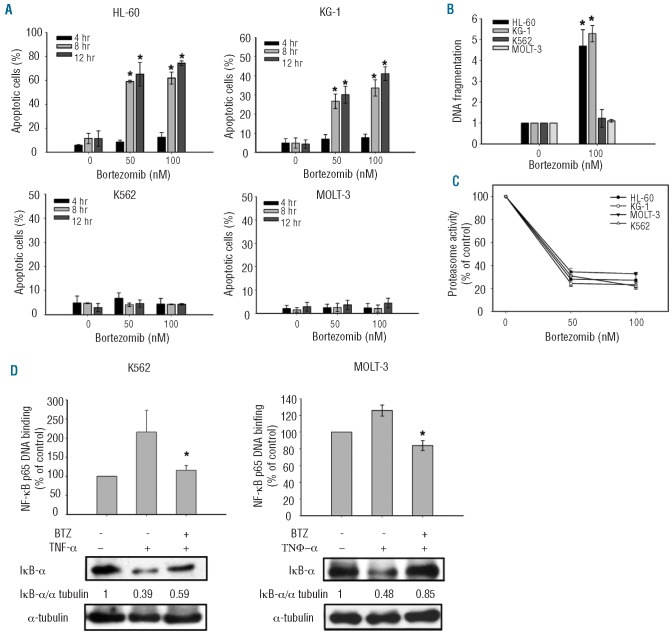
Figure 1.
Differential anti-leukemic effects of bortezomib on leukemia cells. (A) Dose-and time-escalation effects of bortezomib (50 nM or 100 nM) on apoptosis in four leukemia cell lines (HL-60, KG-1, K562, and MOLT-3). Cells were exposed to bortezomib at the indicated doses for 4, 8 and 12 h. Apoptotic cells were determined by flow cytometry. Columns, mean (n=3); bars, SD; *P<0.05. (B) Effects of bortezomib on DNA fragmentation in four leukemia cells. Cells were treated with bortezomib (100 nM) for 12 h and DNA fragmentation was analyzed by using a cell death ELISA kit. Columns, mean (n=3); bars, SD; *P<0.05. (C) Bortezomib exerts efficient and similar dose-dependent effect on proteasome inhibition in the four leukemia cells. Cells were exposed to bortezomib at the indicated doses for 6 h before measurement of proteasome activity. (D) Bortezomib still inhibits the proteasome degradation of IkB (inhibitor of NF-κB) in resistant cells. In resistant K562 (left) and MOLT-3 cells (right), bortezomib abolished the NF-κB activation induced by TNF-α, as evidenced by decreased nuclear NF-κB p65 subunit binding activity, and associated increased IκB-α protein level. Cells were exposed to 20 ng/mL of TNF-α for 1 h and then treated with DMSO or 100 nM bortezomib for 24 h. Nuclear extracts were prepared and assayed for NF-κB p65 subunit binding activity by ELISA kit. Columns, mean (n=3); bars, SD. *P<0.05. Cytoplasmic extracts were prepared and assayed for IκB-α by Western blot. Representative of 3 independent experiments.