Figure 8.
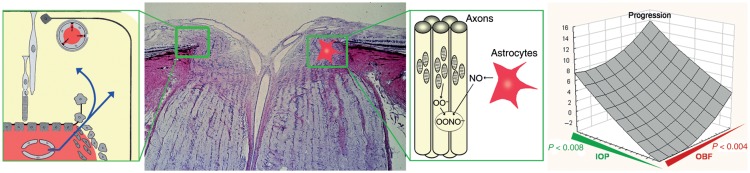
In the optic nerve head (ONH) (second from left), the blood–brain barrier is partly abrogated by the proximity to the fenestrated vessels of the choroid (left). Unstable oxygen supply in glaucoma patients increases superoxide anion (O2−) in the mitochondria of the axons. If neighbouring astrocytes are activated, nitric oxide (NO) diffuses into the axons resulting in the damaging peroxynitrite (ONOO−) (second from right). Indeed, visual field progression in glaucoma patients (right) increases not only with increasing intraocular pressure (green) but also with decreasing ocular blood flow (red). (From Flammer and Mozaffarieh,114 with permission.)
