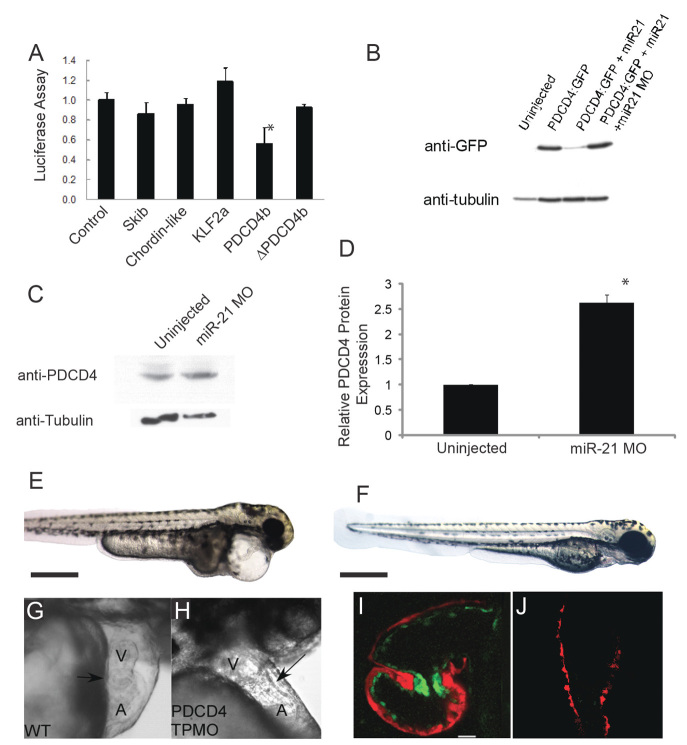
Fig. 3.
pdcd4b is a target of miR-21 during zebrafish valve development. (A) Luciferase assays of candidate miR-21 targets. ΔPDCD4b refers to the pdcd4b 3′ UTR with the miR-21 binding site deleted. Data are mean ± s.d.; *P<0.05. (B) Western blot of whole zebrafish lysates injected at the single-cell stage with mRNA encoding GFP:Pdcd4b, co-injected with miR-21 or with miR-21 plus an miR-21 MO. Tubulin staining serves as a loading control. (C) Representative western blot of endogenous zebrafish Pdcd4 in uninjected and miR-21 morphants. (D) Quantification of zebrafish Pdcd4 western blots demonstrating a significant increase in Pdcd4 when miR-21 is knocked down. Data are mean ± s.d.; *P<0.01. (E-H) Injection of a PDCD4b target protector MO (TPMO) does not perturb the body plan or axis at 72 hpf (E, compared with control F), but does cause pericardial edema, loss of the normal cardiac looping, and AV constriction (G and H, arrow) at 48 hpf. (I,J) Confocal microscopy of the cMLC2:dsRed/Tie2:GFP line shows loss of upregulation of the Tie2:GFP marker (green) in the AV ring in pdcd4-TPmiR-21-injected fish (I, atrium at top, ventricle at bottom) compared with controls (J) at 48 hpf. A, atrium; V, ventricle.