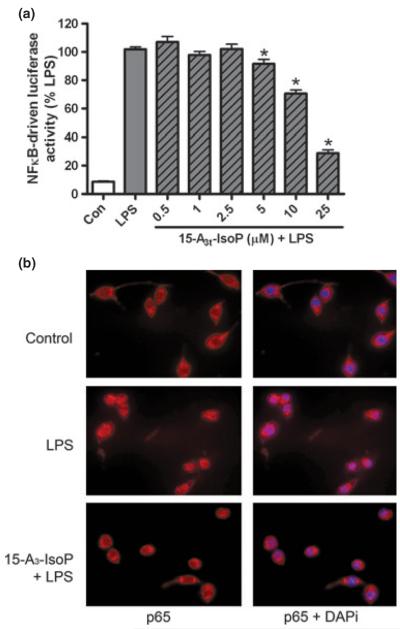
Fig. 3.
15-A3t-IsoP inhibits LPS-induced NFκB nuclear translocation and activation. (a) NFκB reporter macrophages were pre-treated with varying concentrations of 15-A3t-IsoP for 30 min and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 4 h. Luciferase assays were then performed and data represent mean ± SD of five separate experiments; data were normalized to protein concentration expressed as % LPS-induced luciferase activity increase. Statistical analysis of were performed using a one-tailed anova and demonstrated a significant treatment effect with p < 0.01. Post hoc analysis revealed control versus LPS p < 0.001. Asterisks are used to denote statistically significant effects of various concentrations of 15-A3t-IsoP + LPS compared with LPS alone. (b) RAW264.7 cells were pre-treated with vehicle or 15-A3t-IsoP (25 μM) and then stimulated with vehicle or LPS (1 μg/mL) for 1 h. Cells were then subjected to immunofluorescent microscopy following staining of the NFκB p65 subunit (red) and nucleus (DAPI staining, blue).