Fig. 4.
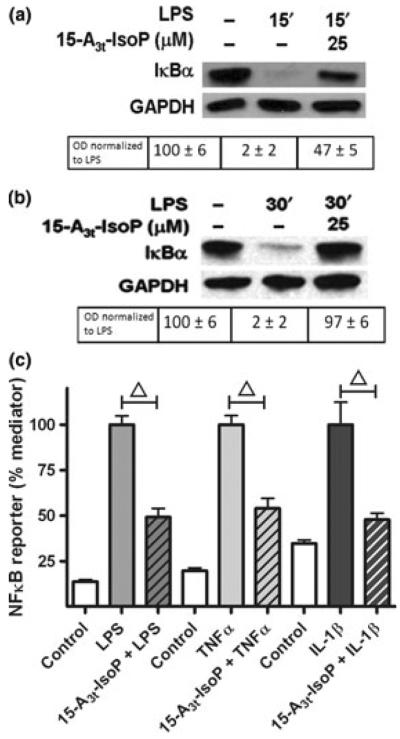
15-A3t-IsoP inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in macrophages at the level of the IκK. (a, b) RAW264.7 macrophages were pre-treated with varying concentrations of 15-A3t-IsoP for 30 min, stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL), and harvested at 15 (a) or 30 min (b). Protein lysates were subjected to western blot analysis with the anti-IκBα-antibody and results are representative of four independent experiments. GAPDH blots are shown as loading controls. Semi-quantitative analysis of optical densities is shown below each group with average ± SD expressed for all analyses. Data in panels (a) and (b) represent four independent experiments. (c) NFκB reporter macrophages were pre-treated with vehicle or 15-A3t-IsoP for 30 min and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL), TNFα (10 ng/mL), or IL-1β (20 ng/mL) for 4 h. Data expressed as % inflammatory mediator-stimulated luciferase activity. Statistical analysis of was performed using a two-tailed between group anova for each treatment (TNFα, LPS or IL1β) and demonstrated a significant treatment effect of each drug group with p < 0.01. Post hoc analysis using Tukey's HSD testing revealed significance of 15-A3t-IsoP addition compared with treatment alone with a p < 0.01 denoted by a bracketed △ representing a p < 0.01.
