Fig. 1.
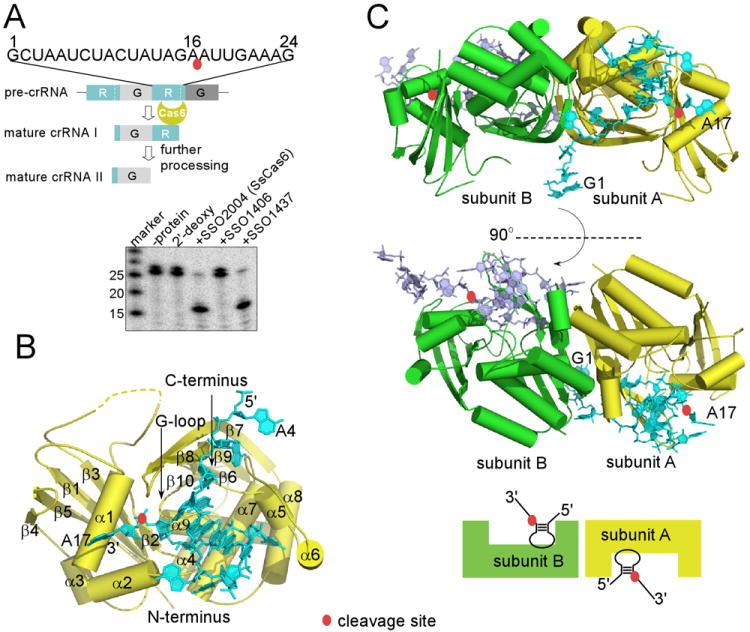
Overview of CRISPR RNA processing activities and structures of SsCas6 bound with a repeat RNA. The scissile phosphate group is indicated by a red oval. (A). Sulfolobus sulfotaricus P2 (Ss) CRISPR RNA processing activities of Ss proteins SSO2004, SSO1437, and SSO1406. The repeat RNA from Ss CRISPR locus F was cleaved by the two close homologs SSO2004 and SSO1437 but not SSO1406 whose sequence clearly distinguishes itself from the other two. “2′-deoxy” denotes the cleavage result with SSO2004 and the same 24mer repeat RNA containing 2′-deoxy modification at position 16. Markers were used to provide relative positions of non-related RNA oligomers. (B). Overview of SsCas6 structure and its complex with the repeat RNA. The structure of SsCas6 in isolation is similar to that bound with RNA and is thus not shown separately here. Secondary structure elements of SsCas6 and the RNA nucleotides are labeled. (C). Two orthogonal views of the dimeric structure of SsCas6 bound with the 24mer noncleavable RNA. The monomeric units are distinguished by different colors.
