Figure 5.
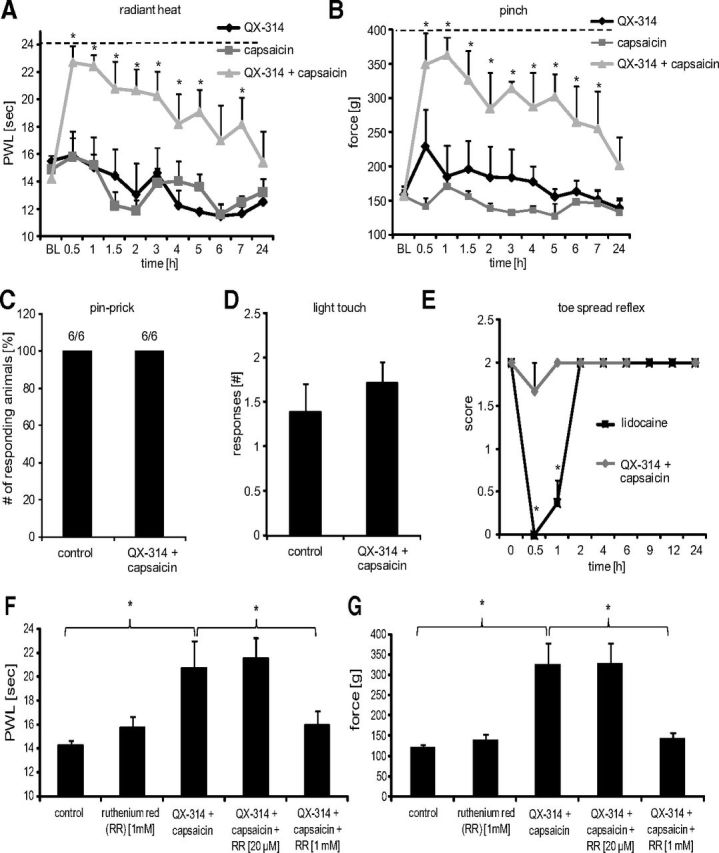
Sensory processing of TRPV1-expressing neurons in naive rats. Behavioral responses were determined after silencing TRPV1-expressing neurons by injection of 200 μl of 0.5% QX-314 followed by 200 μl of 0.05% capsaicin into the sciatic notch. Different sensory stimulations were applied to the lateral paw. A, Thermal thresholds after radiant heat stimuli. At the indicated time points, paw withdrawal latencies were determined using the Hargreaves test. B, Mechanical thresholds after nociceptive stimulation with an increasing force using a pincher. C, Nociceptive responses after mechanical stimuli induced by a pinprick at 1 h after perineural injections. 6/6, Six rats of six showed a rapid withdrawal response. D, Paw withdrawal responses to light touch stimulations with a brush. Average number of responses to five stimulations to the lateral plantar paw was determined at 1 h after perineural injections. E, Motor function. Toe-spread reflexes were scored after perineural injection of lidocaine [2%] or silencing TRPV1-expressing neurons as above: 0, no spreading; 1, intermediate spreading; 2, full spreading. F, G, RR dependence of silencing TRPV1-expressing axons. Rats received perineural injections of 0.5% QX-314 followed by 0.05% capsaicin and ± the indicated RR concentrations. After 1 h behavioral responses to thermal or mechanical stimuli (F, Hargreaves test as in A; G, pinch test as in B) were determined. In all experiments, data represent the average ± SEM from six animals per group. Significance was calculated by the two-way repeated-measures ANOVA and Bonferroni correction. *p < 0.05 compared with saline and vehicle injection. The dashed line indicates the cutoff. PWL, Paw Withdrawal Latency.
