Figure 5.
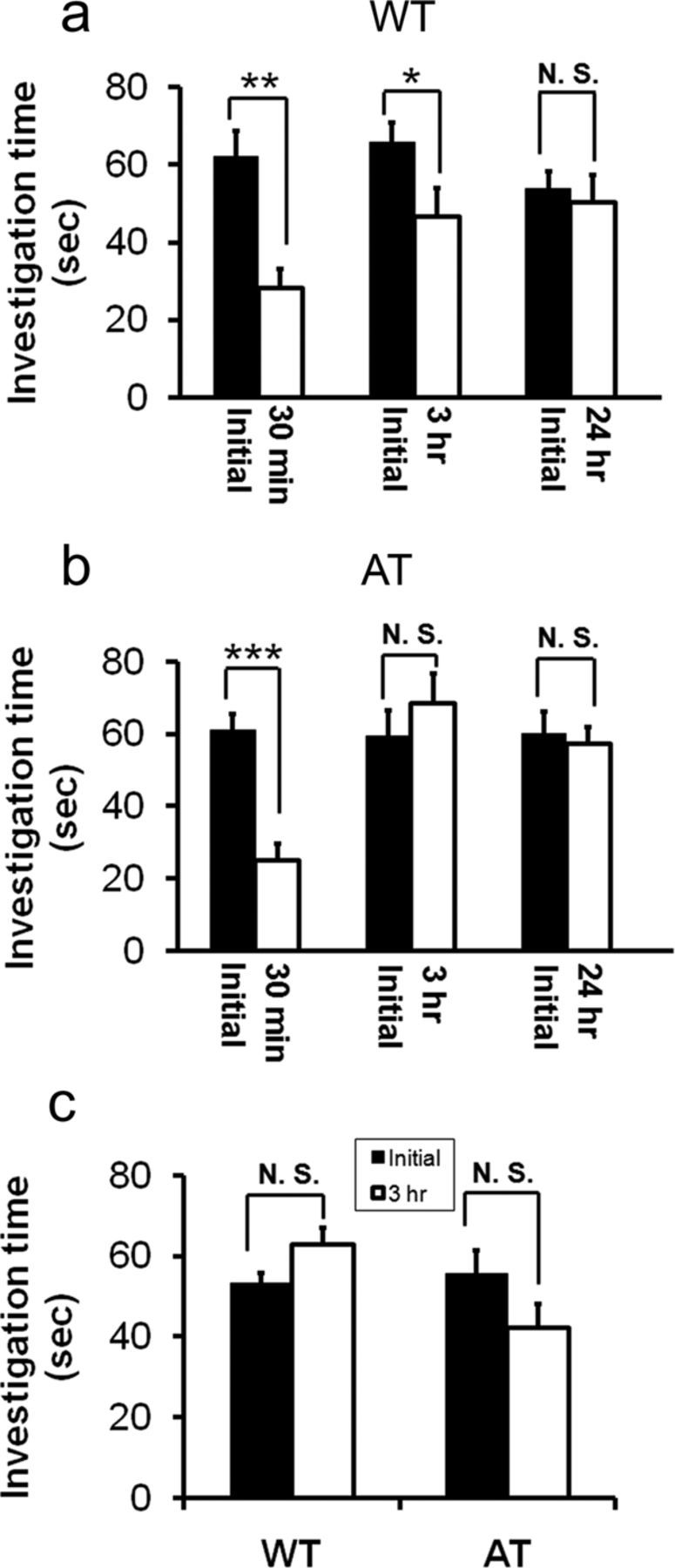
AT mice showed normal social interaction but with a social memory deficit compared with WT littermates in a direct contact social test. a, Test WT mice displayed social approach behavior toward the stimulus mouse (sociability) and reduced the approach behavior toward the reexposed social cue mouse 30 min and 3 h after initial contact as measured by a reduction in investigation time (n = 8 per genotype). Paired Student's t test: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. After a 24 h delay after the initial interaction, the test mouse spent the same amount of time investigating the same social cue mouse as in the initial trial. b, Test AT mice displayed social approach behavior toward the stimulus mouse (sociability) and reduced investigation time toward the same social cue 30 min after the initial interaction (n = 8 per genotype). Paired Student's t test: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. After a delay of 3 or 24 h after the initial interaction, the test mouse spent a similar amount of time investigating the reexposed social cue as in the initial interaction. c, AT and WT mice show similar investigation times toward two different, unfamiliar social cue mice between the initial trial and a second test after a 3 h delay. In the initial contact, the test subject displayed social approach behavior, as indicated by time investigating the stranger mouse. Three hours later, the same test subject was tested for its sociability toward a novel mouse (taken from another homecage). Subjects were 3-month-old male mice (n = 8/genotype). Paired Student's t test, p > 0.05).
