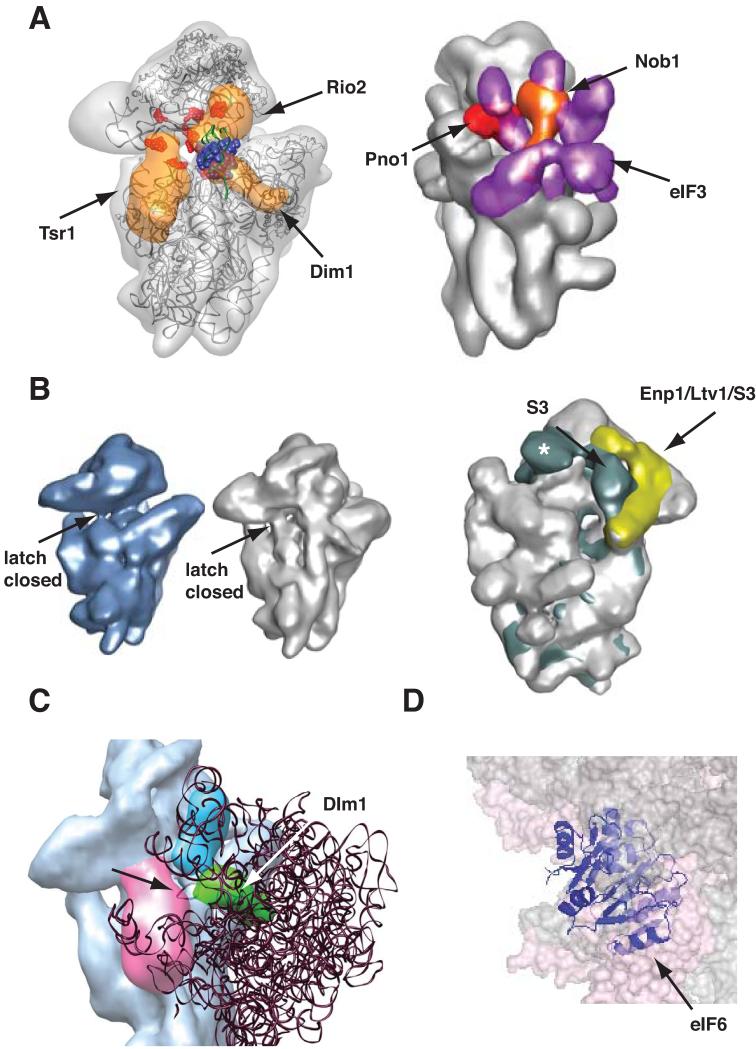
Figure 1.
Assembly Factors Block Premature Translation Initiation. Adapted from [21]. (A) Left: Tsr1, Rio2 and Dim1 on the subunit interface block binding of eIF1 (in blue spacefill, [100]), eIF1A (binding site highlighted in red, [101]), and P-site tRNA (in green, [102]). Right: Nob1 (orange) and Pno1 (red) block binding of eIF3 (purple, [103]). (B) Opening of the mRNA binding channel is destabilized. The entry latch on the mRNA binding channel (indicated with the arrow) is closed in mature 40S subunits (left, [28]) and pre-40S subunits (middle, [21]). Channel opening in mature subunits (right panel) is stabilized by an interaction between S3 and H16 (shown in dark green, [28]) on the solvent side. The AFs Enp1 and Ltv1 form a complex with S3 (in yellow, [21]), which does not allow for this interaction of S3. Asc1, present only in mature 40S subunits, is indicated with a white asterisk. (C) In 80S ribosomes the A-site finger from the 60S subunit (indicated with the arrow), overlaps with H44 and Dim1 (in green), but not Tsr1 (in magenta). (D) In 80S ribosomes eIF6 (in purple, [37]) overlaps with the 40S subunit (shown in spacefill, [104]). For simplicity the 60S subunits is not shown.