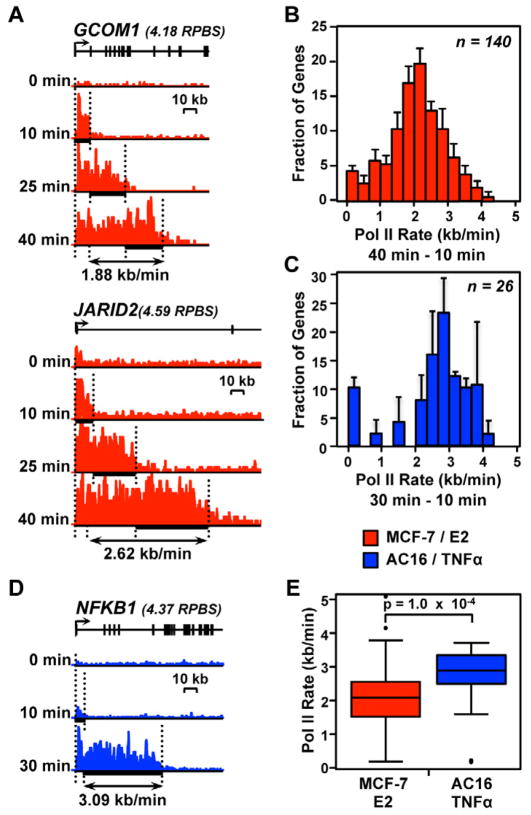
Figure 2. Pol II transcription rates vary across the genome and between different biological systems and inducers.
(A and D) Pol II density following a time course of treatment with inducer. (A) Red, two genes responding to E2 treatment in MCF-7 cells. (B) Blue, a gene responding to TNFα treatment in AC16 cells. Different time points are shown at the same Y-axis scale for each gene. Y-axes vary between genes based on their expression level, which are shown in units of reads per base scaled (RPBS) above each gene.
(B and C) Histograms of Pol II elongation rates for 140 genes in MCF-7 cells (B) or 26 genes in AC16 cells (C) for which high confidence elongation rates could be determined. Error bars represent standard error of the mean between biological replicates.
(E) Comparison of elongation rates between MCF-7 and AC16 cells. The p-value was calculated using a two-sided Wilcoxon rank sum test.