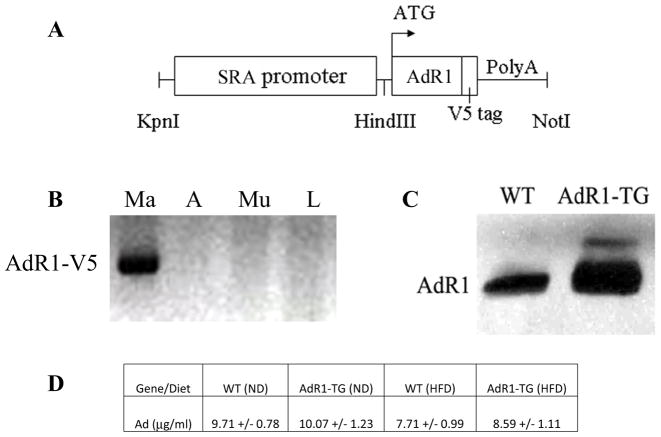
Fig. 1. Macrophage AdipoR1 transgenic mice.
(A) DNA construct for AdipoR1 macrophage-specific targeting with a human scavenger receptor A-I gene (SR-AI) enhancer/promoter and growth hormone tail with poly A. (B) Mouse tissues were isolated and collected from AdipoR1 transgenic mice at six weeks of age, and AdipoR1 transgene expression was examined with RT-PCR analysis using a primer pair which amplified the junction sequences between the AdipoR1 gene coding region and the V5 epitope tag. The labeling of samples indicated as Ma (macrophage), A (adipose tissue), Mu (skeletal muscle), and L (liver). (C) AdipoR1 protein levels in macrophages were examined in control wild-type (WT) and AdipoR1 transgenic (AdR1-TG) mice (n=8 for each group) at six weeks of age by Western blot analyses with an AdipoR1 antibody (Abcam). Each lane was loaded with 20 μg of total cellular protein extracted from the macrophages. (D) Circulating total adiponectin (Ad) levels were quantitatively analyzed in wild-type (WT) and AdipoR1 transgenic (AdR1-TG) mice (n=6 for each group) aged at 20 weeks under normal diet (ND) or high fat diet (HFD) condition using an ALPCO ELISA kit.