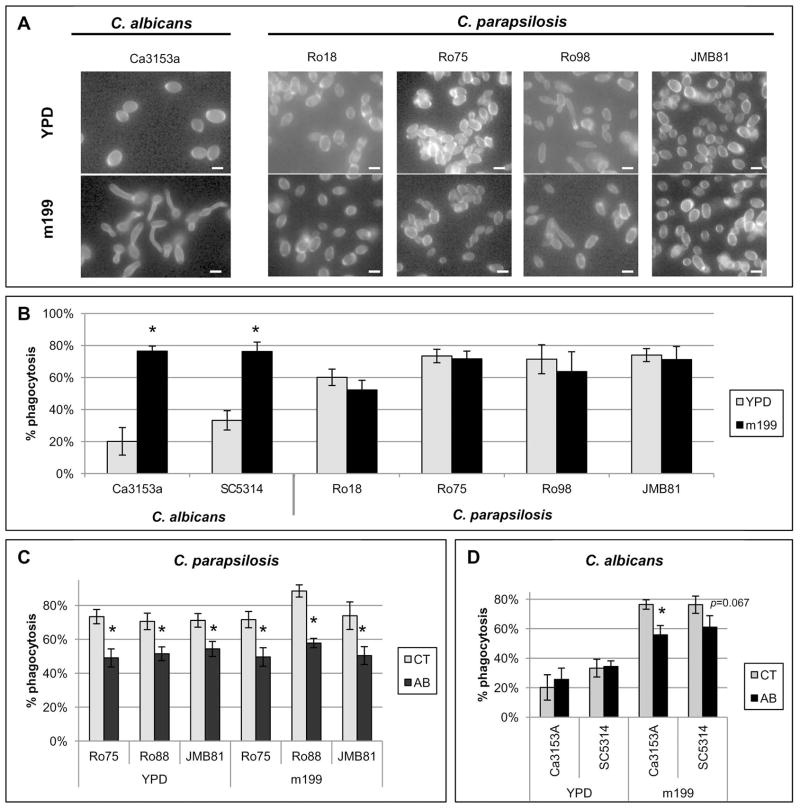
Figure 3. Evaluation of additional C. albicans and C. parapsilosis stains.
Results are mean ± SEM of at least two separate neutrophil donors in three separate experiments. Between-group comparisons were made by the Fisher LSD test. * p ≤ 0.05. (A) Photomicrographs of C. albicans or C. parapsilosis strains grown as yeast in YPD broth or grown in medium 199 (m199) to induce germ tube formation. Cells were stained with Calcofluor White to facilitate imaging. C. albicans exhibited germ tube growth while C. parapsilosis strains exhibited no detectable morphological change. Bar = 4 microns. (B) Neutrophil phagocytosis rates of C. albicans and C. parapsilosis grown in YPD or m199 at an E:T of 1:10. (C–D) Neutrophil phagocytosis rates of selected C. parapsilosis strains (C) or C. albicans strains (D) grown in YPD or m199 at an E:T of 1:10. Phagocytosis rates of untreated neutrophils (CT) were compared to phagocytosis rates of neutrophils treated with gal3 blocking antibody (AB).