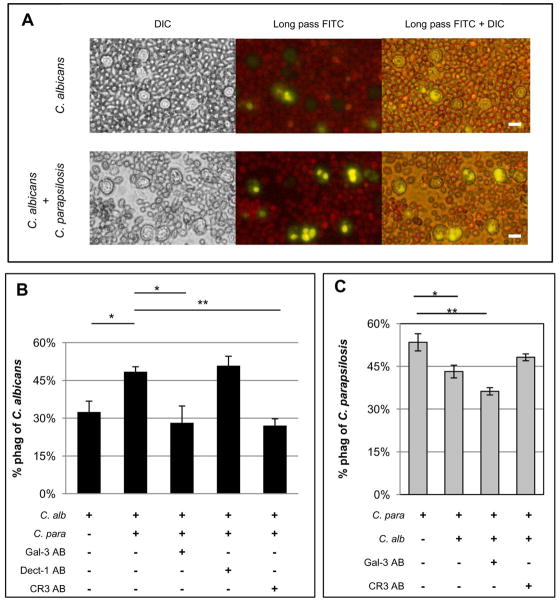
Figure 6. Exposure of neutrophils to C. parapsilosis increases phagocytosis of C. albicans.
All images are representative fields of at least three different donors and results are mean ± SEM of at least three different donors. *p≤0.05, **p≤ 0.005. Bar = 10 microns. (A) Images of neutrophil phagocytosis of C. albicans labeled yellow when incubated alone (top panel) or in combination with unlabeled C. parapsilosis (bottom panel). (B) Neutrophil phagocytosis rates of C. albicans (C. alb) when incubated alone, coincubated with C. parapsilosis (C. para), or coincubated with C. parapsilosis after neutrophils were pretreated with blocking antibodies against gal3 (Gal-3 AB), dectin-1 (Dect-1 AB), or CR3 (CR3 AB). (C) Neutrophil phagocytosis rates of C. parapsilosis (C. para) when incubated alone, coincubated with C. albicans (C. alb), or coincubated with C. albicans after neutrophil pretreatment with blocking antibodies against gal3 (Gal-3 AB) or CR3 (CR3 AB).