Figure 6. Effects of ad libitum feeding and L-FABP gene ablation on the expression levels of important enzymes in mitochondrial oxidation as well as on serum levels of β-hydroxybutyrate.
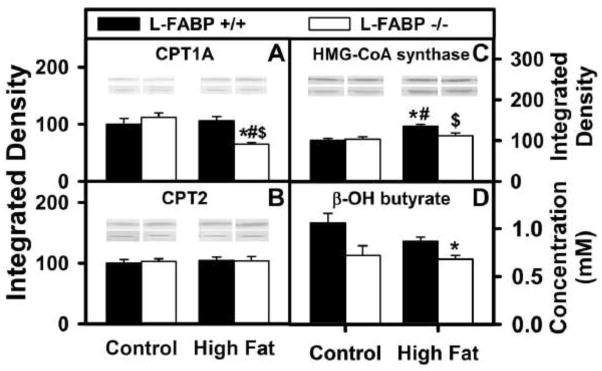
After the end of the 12 wk dietary study, livers from L-FABP (+/+) and L-FABP (−/−) mice fed control or high-fat diets ad libitum were harvested and expression of the key mitochondrial LCFA β-oxidation enzymes was measured by western blotting as described in Methods. The effect of L-FABP gene-ablation on (A) carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1 (CPT1), (B) carnitine palmitoyl transferase-2 (CPT2), and (C) HMG-CoA synthase was examined. At the end of the dietary study, serum was also collected and levels of β-hydroxybutyrate were measured for L-FABP(+/+) and L-FABP(−/−) mice ad libitum-fed control and high-fat diets (D) as described in Methods. Representative western blots were included of each respective protein (lower lane) and normalization protein (upper lane). Values represent the mean ± SEM, n=5–8. Statistical analysis performed by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. The significance was as follows: * p ≤ 0.05 as compared to L-FABP (+/+) control diet; # as compared to L-FABP (−/−) control diet; and $ as compared to L-FABP (+/+) high-fat diet.
