Figure 1.
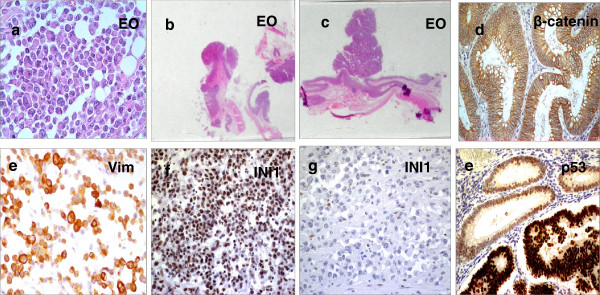
Immunohistochemical markers of colon carcinoma with rhabdoid features, adjacent adenomas and normal mucosa. (a) Hematoxylin&Eosin staining of the rhabdoid component in the composite RCT (case II) (b). Low-power view of tubular adenomas and (c) a larger dysplastic adenoma with a cancerized component contiguous to the main tumor mass of the composite RCT. (d) Membrane β-catenin staining in the large dysplastic adenoma adjacent to the composite RCT. (e) Intense and diffuse vimentin immunohistochemical staining in rhabdoid cells of pure RCT (case I) (f) Intense INI1 nuclear immunostaining in rhabdoid cells of case I (g) Loss of INI1 staining in the rhabdoid component of composite RCT showing appropriate staining of intratumoral lymphocytes serving as internal control. (h) A strong nuclear p53 staining marks the transition from adenoma to carcinoma in larger dysplastic polyps. Magnification (×200 or ×400).
