Figure 3.
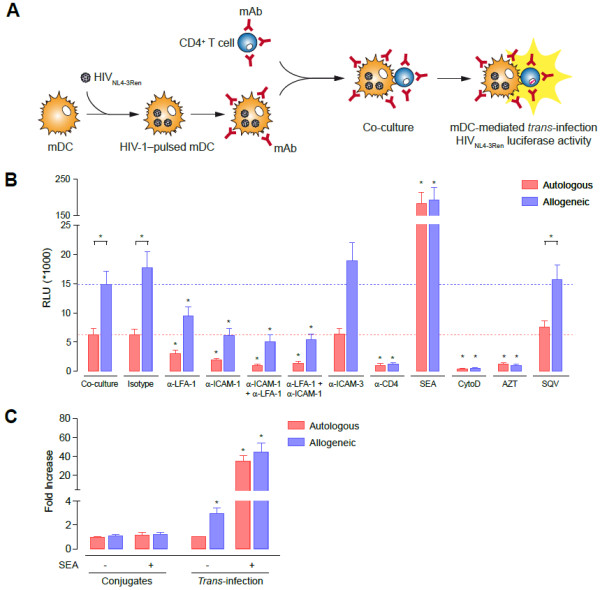
mDC-mediated HIV-1 trans-infection to primary CD4+ T cells is dependent on the interaction between ICAM-1-LFA-1 and is enhanced by antigen recognition. A. Experimental procedure for quantification of mDC-mediated trans-infection of the infectious reporter virus HIVNL4-3Ren to non-activated CD4+ T cells in the presence of several reagents. B. Comparative HIV-1 mDC-mediated trans-infection of non-activated CD4+ T cells in autologous or allogeneic co-cultures in the presence of several reagents. Allogeneic co-cultures (blue bars) led to a three-fold increase in productive HIV-1 replication compared with autologous co-cultures (red bars) (p < 0.05). Blocking ICAM-1 and LFA-1 with mAb significantly inhibited the mDC-mediated HIV-1 trans-infection. The α-ICAM-1 + α-LFA-1 condition represents separate pre-incubation of mDC with α-ICAM-1 mAb and CD4+ T cells with α-LFA-1 mAb, before launching co-culture, whereas the α-LFA-1 + α-ICAM-1 condition designates separate pre-incubation of mDC with α-LFA-1 mAb and CD4+ T cells with α-ICAM-1 mAb. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared with negative controls (p < 0.05); mAb conditions were compared with the isotype control, whereas AZT, SQV, SEA and cytochalasin D were compared with medium. Data are expressed as mean and SEM from three independent experiments including cells from at least six different donors. RLU, relative light units. C. Fold increase of conjugate formation and mDC-mediated HIV-1 trans-infection in autologous and allogeneic mDC-CD4+ T cell co-cultures in the presence or absence of SEA. All conditions were compared to autologous co-cultures without SEA, shown as unity in the plot.
