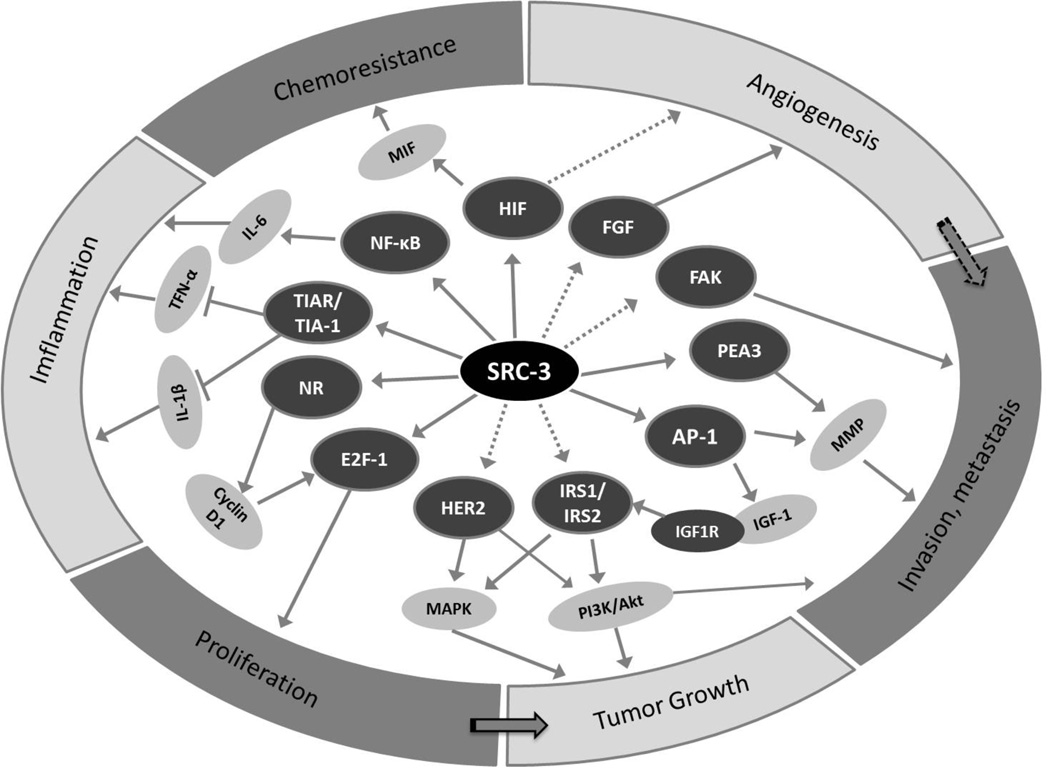
Figure 2. SRC-3 integrates multiple signaling pathways.
Depending on the cellular context, SRC-3 can coactivate different nuclear receptors and transcription factors to promote multiple hallmarks of cancer. SRC-3 classically facilitates the transcriptional activities of nuclear receptors to promote cell growth. It also coactivates E2F-1 to promote cell division. To impact on tumor expansion, SRC-3 serves as a coactivator for AP1 to upregulate IGF-Akt pathway and may be involved in HER2 pathway. SRC-3 also acts as a pro-metastatic factor by coactivating PEA3 and AP1 to upregulate MMP production, a requisite process in extracellular matrix breakdown that accompanies invasive tumor behavior. A spliced SRC-3 isoform located in cytoplasm can also contribute to metastasis by serving as an adaptor for FAK-Src signal pathway. SRC-3 has been implied to bind NFκB and upregulate MIF through the HIF transcription factor. This, in turn, contributes to chemoresistance, as well as angiogenesis through the FGF signaling pathway. NR, nuclear receptor such as ER, PR or AR. The solid arrow indicates direct interaction or known pathways while the dotted arrow indicates indirect interaction.