Figure 1. Expression of oncogenic K-Ras promotes the activation of WT H-Ras through the allosteric stimulation of Sos.
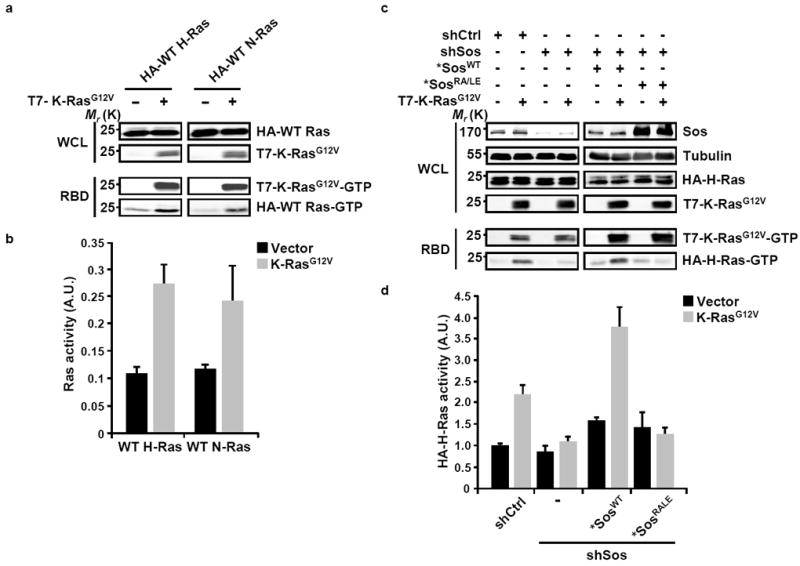
(a) HeLa cells were transfected with HA-tagged wild type (WT) Ras isoforms either alone or with T7-tagged K-RasG12V construct as indicated. Following serum starvation, the levels of GTP-bound WT and oncogenic Ras were determined by the RBD pull-down assay and were detected using anti-HA or anti-T7 antibodies, respectively. (b) The levels of activated Ras were quantified by densitometry scanning and normalized to the total levels of the respective isoform. Values are means +/- SD from three independent experiments. (c) HeLa cells were transfected with pSuper constructs expressing scrambled shRNA (shCtrl) or shRNA targeting Sos (shSos). Cells were selected with blasticidin S for 3 days and then transfected with HA-H-Ras and, as indicated, T7-K-RasG12V constructs in the absence or presence of shRNA-resistant WT or RA/LE Sos constructs (*SosWT and *SosRA/LE). Following serum starvation for 20 h, the levels of GTP-bound HA-H-Ras and T7-K-Ras were determined by the RBD pull-down assay and were detected using anti-HA and anti-T7 antibodies, respectively. (d) Quantification of H-Ras-GTP was carried out by densitometry scanning and data was normalized to the levels of total HA-H-Ras. Values are means +/- SD from three independent experiments presented as fold activation compared to shCtrl vector. For all panels, the efficiency of Sos suppression was analyzed by western blotting and tubulin was used as a loading control. WCL, whole cell lysate; A.U., arbitrary units.
