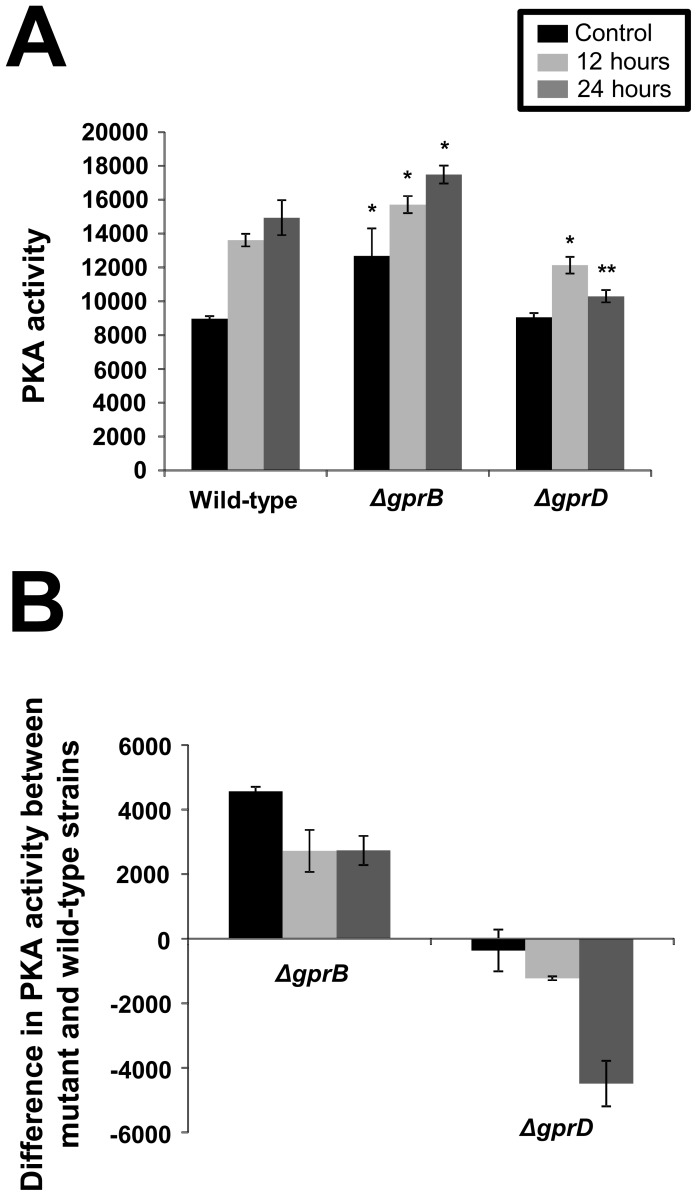
Figure 4. Determination of the protein kinase A activity for the wild-type, ΔgprB and ΔgprD mutant strains.
Protein kinase A (PKA) activity is increased and decreased in the ΔgprB and ΔgprD mutant strains, respectively, upon carbon starvation. These three strains were grown for 24 hours in liquid minimal medium supplemented with 2% glucose. Then, their mycelia were transferred to liquid minimal medium without carbon source for 12 and 24 hours. The control represents PKA activity before transferring the mycelia to liquid medium without any carbon source. (A) Absolute levels of PKA activity from cultures of the wild-type, ΔgprB, and ΔgprDmutant strains for control MM+2% glucose) and carbon-starved for 12 and 24 hours. (B) Difference in PKA activity between the wild-type strain and ΔgprB and ΔgprDmutant strains. One unit of kinase activity is defined as the number of nanomoles of phosphate transferred to a substrate per minute per milliliter. The t-test was used to compare the mutant strains with the wild-type strain (p-value<0.05, **, and<0.01 *).