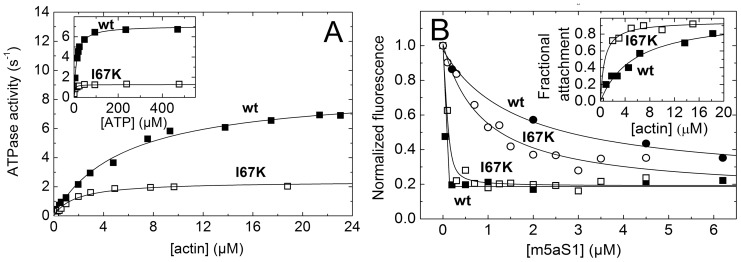
Figure 4. I67K mutant exhibits slowed actin-activated ATPase activity and high steady-state actin attachment.
A, Actin (main panel) and ATP (inset) concentration dependence of wt-m5aS1 (solid squares) and I67K-m5aS1 (open squares) steady-state ATPase activity (concentrations used: 100 nM m5aS1 (both panels), 1 mM ATP (main panel), 10 µM actin (inset)). Hyperbolic fits to the datasets shown yielded maximal activities (k cat) of 8.7 and 2.4 s−1 with half-saturation (K actin) at 5.6 and 1.8 µM actin (main panel); and 7.1 and 1.3 s−1 with half-saturation (K ATP) at 12 and 2.8 µM ATP (inset) for wt-m5aS1 and I67K-m5aS1, respectively. B, Main panel, wt-m5aS1 (solid symbols) and I67K-m5aS1 (open symbols) concentration dependence of fluorescence intensities of 150 nM PA in the absence of nucleotide (rigor, squares) and in 1 mM ATP (circles). Quadratic fits to the rigor datasets (based on an equation described in [40]) and hyperbolic fits to the ATP datasets shown yielded apparent m5aS1 binding K d values and m5aS1-saturated PA fluorescence levels (normalized to that in the absence of m5aS1) of less than 0.5 µM and 0.19 (for both wt-m5aS1 and I67K-m5aS1 in rigor); 1.7 µM and 0.23 (wt-m5aS1 in ATP); and 0.88 µM and 0.14 (I67K-m5aS1 in ATP). Inset, actin concentration dependence of the fractional actin attachment of 1 µM wt-m5aS1 (solid squares) or I67K-m5aS1 (open squares) in the presence of 15 mM ATP, determined in acto-m5aS1 cosedimentation experiments. Hyperbolic fits to the datasets indicated half-saturation at 5.5 and less than 2 µM actin for wt-m5aS1 and I67K-m5aS1, respectively.