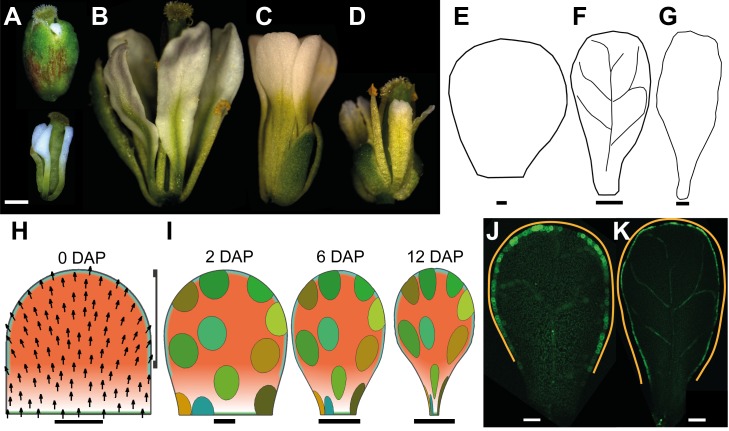
Figure 10. Effect of extending the DGRAD and distal organiser domains.
(A) Ectopic JAG line (AP1>>JAG) flower with a strong phenotype in which sepal organs are fused and petal organs are reduced or deformed (same flower is shown with or without sepals). (B) Ectopic JAG line flower with an intermediate phenotype in which petals have a different shape, as if the region of the petal with distal identity has extended more proximally. (C) Wild-type flower with paddle shape petals. (D) jag-1 mutant flower with petals with a reduced distal region. (E–G) Representative petal outlines from intermediate phenotype lines at various stages of development. Width of petals: 115 µm (E), 294 µm (F), 940 µm (G). (H) Initial canvas for divergent petal model with a proximally extended DGRAD region (terracotta, bracket indicates plateau of maximum DGRAD), and an extended DISTORG (cyan) region. The polarity field diverges at more proximal positions than in the wild-type model (compare with Figure 4D,E). (I) Model output at 2, 6, and 12 DAP showing patterns of virtual clones induced at 0 DAP and broadening of more proximal regions compared to the model for wild type (Figure 4J). (J, K) DR5::GFP expression in the intermediate phenotype ectopic JAG line extends more proximally compared with wild type (Figure 5G–I). The orange line indicates the extent of the DR5 signal. Width of petals: 139 µm (J), 294 µm (K). Scale bar, 10 µm (E, H, I) (2 DAP), 20 µm (J), 50 µm (K), 100 µm (F, I) (6 DAP), 200 µm (G), 500 µm (A–D), 1 mm (I) (12 DAP).