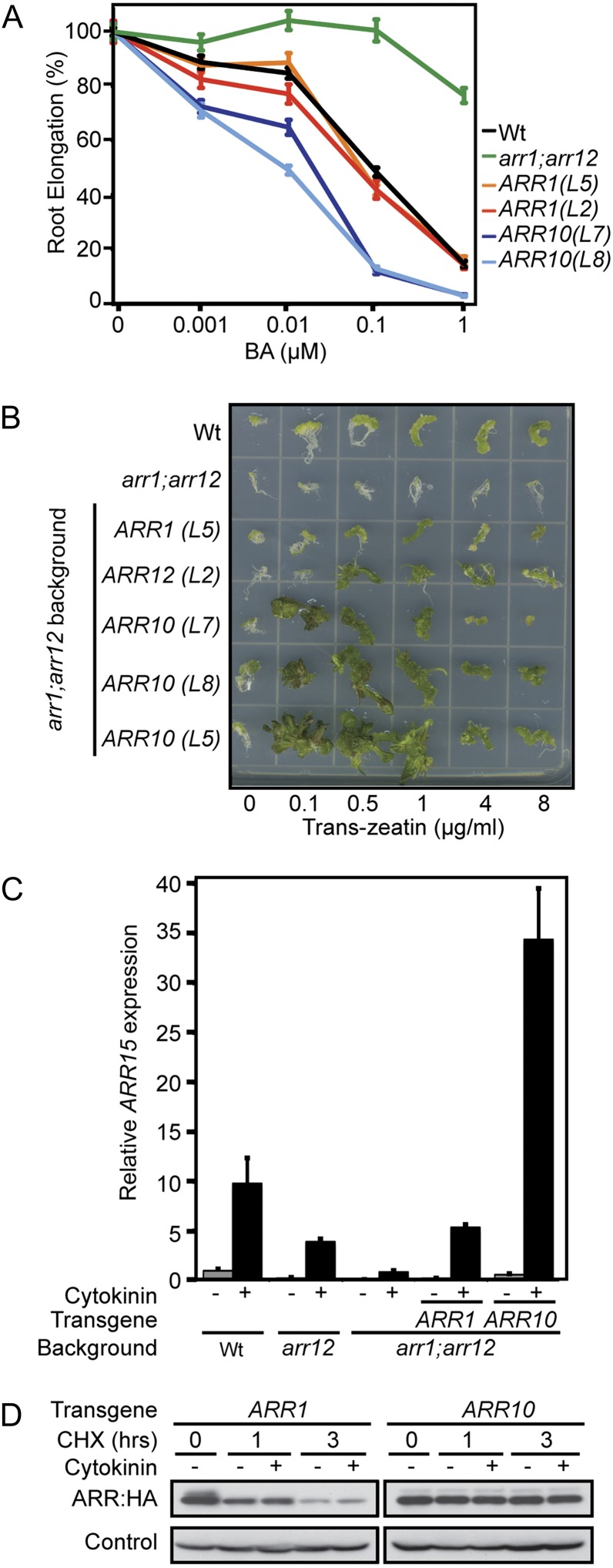
Figure 4.
ARR10 confers cytokinin hypersensitivity when expressed in the same context as ARR1. A, The root elongation response of seedlings grown on media containing 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, and 1 μm BA are expressed as a percentage of the root growth of siblings grown on DMSO control media. Root growth was measured from day 4 through day 7. Error bars indicate se. The mean root growth measurements from untreated lines were 21.1 mm (wild type), 22.4 mm (arr1 arr12), 18.6 mm (tARR1 L2), 19.5 mm (tARR1 L5), 19.2 mm (tARR10 L7), and 19.2 mm (tARR10 L8). B, Induction of callus formation and greening. Representative hypocotyl segments treated with 0.2 mg L–1 indole-3-butyric acid and the indicated concentrations of trans-zeatin are shown after growth for 3 weeks under constant light. C, Relative ARR15 transcript levels in RNA isolated from roots of 14-d-old seedlings treated for 2 h with 10 µm BA or a DMSO control. β-tubulin-3 (At5g62700) was used as an internal control. Transgenic lines tARR1 L5 and tARR10 L7 were examined. D, Protein levels and degradation of ARR1 and ARR10 proteins in Arabidopsis protoplasts. Equal quantities of ARR1 and ARR10 plasmids were transfected into protoplasts. The transfected cells were treated with cycloheximide to inhibit protein biosynthesis, in the absence (–) or presence (+) of trans-zeatin, for the indicated times. ARR1 and ARR10 protein levels were determined by immunoblot analysis with an anti-HA antibody. α-Tubulin protein was immunologically detected as the loading control. Wt, Wild type; CHX, cycloheximide.