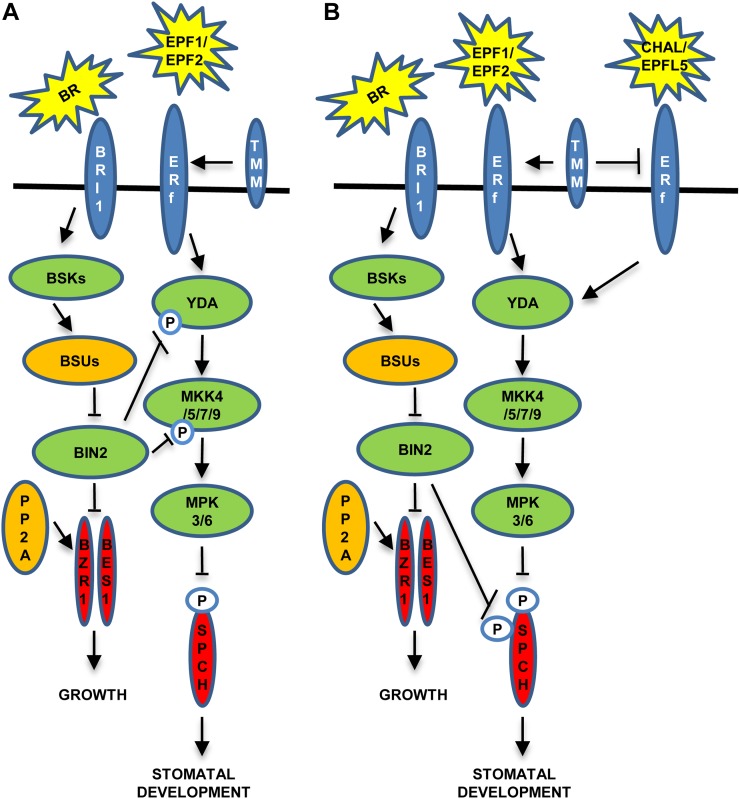
Figure 1.
Proposed cross talk between BRs and stomatal development. A, Regulation of stomatal formation in the cotyledon. TMM enhances EPF1 and EPF2 signaling through ERf. At low BR levels, BIN2 phosphorylates and inactivates both YDA and MKK4, switching off the signaling that inactivates SPCH by phosphorylating residues in the MPKTD, which triggers stomatal production. Genetic data also suggest that ERf and TMM regulate BIN2 (or upstream components). B, Stomatal formation in the hypocotyl. TMM enhances EPF1 and EPF2 signaling, but also dampens CHAL and EPFL5 signaling. TMM action reduces EPF1 and EPF2 signaling, leading to a reduction of MAPK activity. Under this scenario, in the absence of BRs, BIN2 inactivates SPCH by phosphorylating residues in the N terminus and in the MPKTD. These phosphorylation events repress stomatal development.