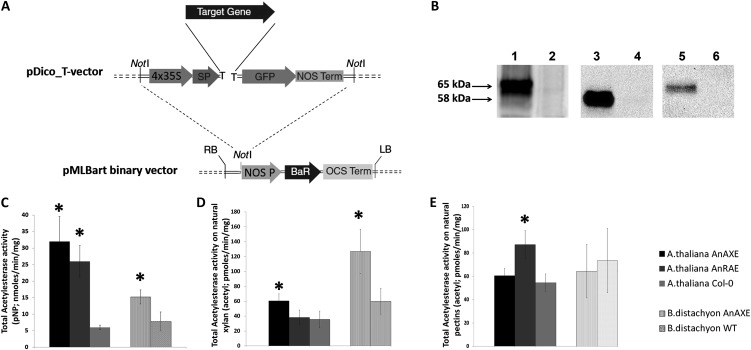
Figure 1.
A, The expression cassette of the vector developed for Arabidopsis transformation. BaR, Gene for herbicide resistance (Basta; dl-phosphinothricin); LB, left border; NOS Prom, promoter from nopaline synthase; NOS Term, terminator from nopaline synthase; OCS Term, octopine synthase terminator; RB, right border; SP, Arabidopsis expansin-B signal peptide; Target Gene, gene of interest; 4x35S, tetramer of the CaMV 35S RNA promoter. B, Western-blot analysis of total proteins from apoplast of transgenic and wild-type plants. On the left, the arrows show the size of proteins in kD. Lane 1, Arabidopsis plant expressing AnAXE fused with GFP (65 kD); lane 3, Arabidopsis plant expressing AnRAE fused with GFP (58 kD); lane 5, Brachypodium plant expressing AnAXE fused with GFP (65 kD); lanes 2, 4, and 6 represent total protein from wild-type plants prepared in parallel with transgenic plant protein extracts. Equal amounts of total protein were loaded for each line, and expressed proteins were detected using GFP monoclonal antibodies (1:5,000 dilution). C, Esterase activities in apoplast from transgenic and wild-type (WT) plants (pNP-acetyl was used as a substrate). D, Esterase activities in apoplast from transgenic and wild-type plants estimated using birch wood xylan. E, Esterase activities in apoplast from transgenic and wild-type plants determined using citrus pectin. In all assays, apoplast fluids were prepared from the combined three plants for each of three independent transgenic homozygous lines, of three lines expressing empty vector, and of three Col-0 plants, all of the same age. Bars represent mean ± sd of total acetylesterase activity averaged for three independent transgenic lines. Data represent average values obtained for three independent transgenic lines. Asterisks indicate data sets significantly different between transgenic plants and wild-type plants (Student’s t test, P < 0.05; n = 3).