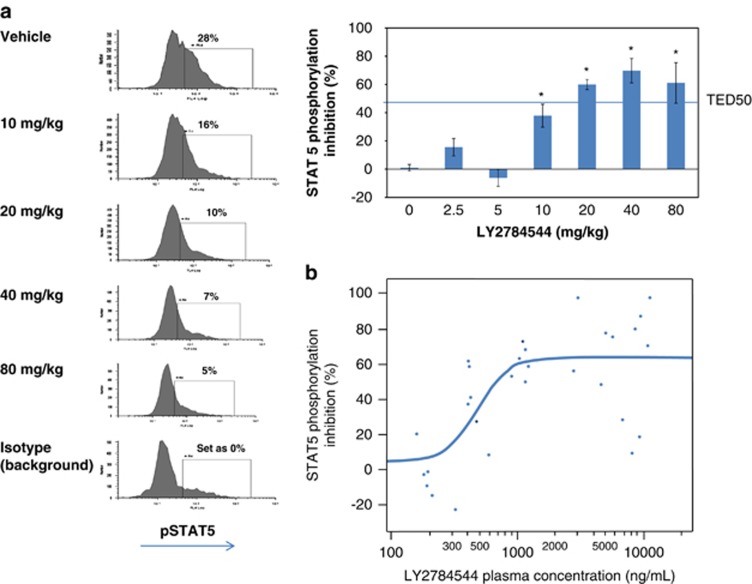
Figure 4.
LY2784544 effectively inhibits JAK2V617F-STAT5 signaling in ascitic tumor cells from Ba/F3-JAK2V617F-GFP tumor-bearing mice. (a) Dose-dependent inhibition of JAK2V617F STAT5 signaling. Oral LY2784544 was administered at the indicated doses, with ascitic cells harvested 30 min later and STAT5 phosphorylation measured by FACS. Left: representative histograms showing decreased pSTAT5Y694-positive ascitic tumor cells collected from animals treated with LY2784544 in dose-dependent manner. Right: quantification of decreased pSTAT5Y694-positive ascitic tumor cells shown in the histograms. The horizontal line indicates the threshold effective dose (TED50). Standard error is indicated by the error bars with statistically significant inhibition, defined as P<0.05 using Dunnett's test, indicated by an asterisk (*). (b) Plasma concentration–dependent inhibition of JAK2V617F activation. Blood was collected 30 min after oral LY2784544 exposure, and the concentration of LY2784544 was measured in the plasma and plotted versus percentage inhibition of STAT5 phosphorylation. Ba/F3, murine pro-B-cells; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; GFP, green fluorescent protein; JAK, janus kinase; STAT5, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5. TED50, threshold effective dose required to cause 50% inhibition.