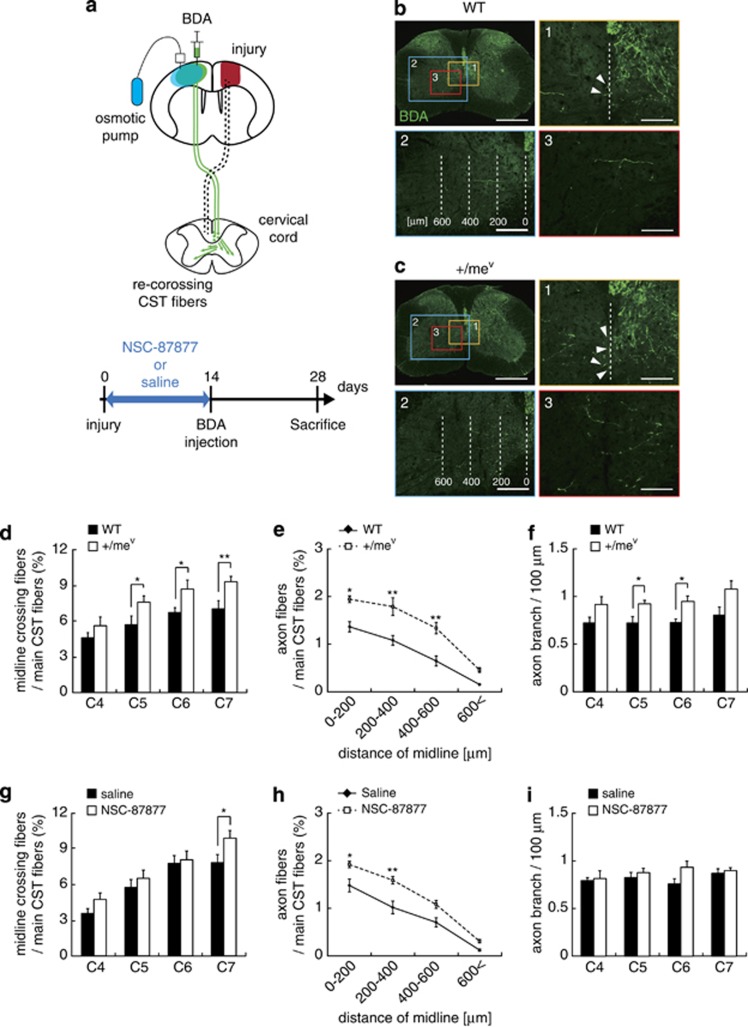
Figure 3.
Inhibition of SHP-1 activity promotes CST sprouting after cortical injury. (a) Schematic illustration of the cortical injury model in this study. Cortical injury to the sensorimotor cortex (red) damages the CST (dotted lines). Saline or NSC-87877 (SHP inhibitor) was continuously infused for 14 days. The anterograde tracer BDA was injected into the contralesional motor cortex to label the intact CST 2 weeks after injury. The green arrows indicate sprouting axons of the intact CST crossing the midline into the denervated side. (b and c) Transverse cervical cord sections showing BDA-labeled CST axons (green) 28 days after cortical injury in wild-type (b) and +/mev mice (c). Scale bars, 500 μm. (1) Arrowheads indicate midline-crossing CST fibers. Scale bars, 100 μm. (2) The white dashed lines indicate the distance from midline, and axonal fibers of uninjured CST in the denervated side were quantified in each area. Scale bars, 200 μm. (3) Axon branches of uninjured CST fibers in the denervated side. Scale bars, 100 μm. (d and g) Quantitative data of the number of CST axons crossing the midline in wild-type and +/mev mice (d) or saline- and NSC-87877-treated mice (g). Data are presented as mean±S.E.M. (wild-type, n=8; +/mev, n=10; saline, n=7; NSC-87877, n=7). *P<0.05, Student's t-test. (e and h) Quantitative data of axon fibers of the uninjured CST in the denervated side at C7 in wild-type and +/mev mice (e) or saline- and NSC-87877-treated mice (h). Data are presented as mean±S.E.M. (wild-type, n=5; +/mev, n=5; saline, n=7; NSC-87877, n=7). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer test. (f and i) Quantitative data of the number of axon branches in the denervated side in wild-type and +/mev mice (f) or saline- and NSC-87877-treated mice (i). The branches were quantified 4 weeks after injury. Data are presented as mean±S.E.M. (wild-type, n=5;+/mev, n=5; saline, n=5; NSC-87877, n=5). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, Student's t-test